Leonardo da Vinci: The Genius of the Renaissance

Introduction
One of the brightest minds in history was Leonardo da Vinci. He was a thinker, an inventor, and a painter. Through his ideas and creations, Leonardo da Vinci altered the course of history.
He had an insatiable curiosity. He studied anatomy, science, engineering, and the arts. Generations were inspired by Leonardo da Vinci’s inventiveness and vision.
The life and works of Leonardo da Vinci are examined in this article. It discusses his formative years, artwork, innovations, and legacy. We’ll find out why people still remember him today.
Leonardo da Vinci: Early Life and Education

In 1452, Leonardo da Vinci was born in Vinci, Italy. He was a notary’s illegitimate son. Caterina was a peasant woman who was his mother.
He didn’t have much formal schooling. As a boy, however, he demonstrated exceptional talent. Leonardo da Vinci cherished drawing and the natural world.
He started working as an apprentice at the age of 14. In Florence, he received instruction from Andrea del Verrocchio. He studied engineering, painting, and sculpture there.
He outperformed his master in no time. His abilities gained widespread recognition in the city. Early in life, Leonardo da Vinci established a solid reputation.
Artistic Masterpieces
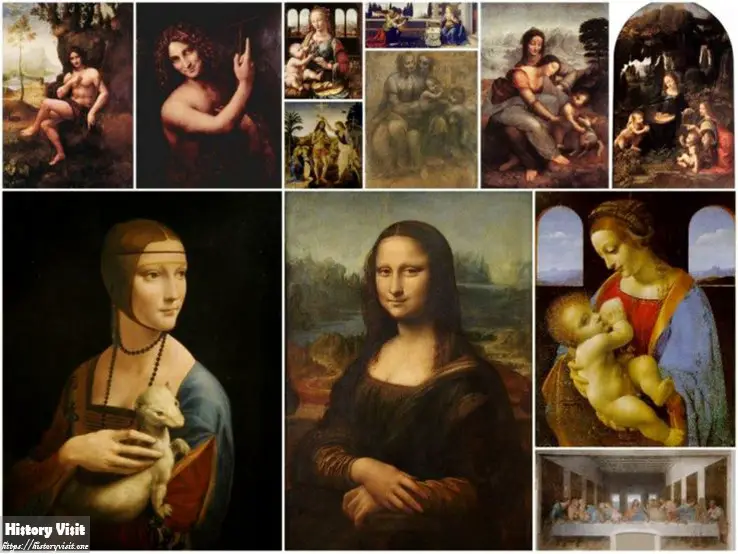

Some of the most well-known paintings in the world were produced by Leonardo da Vinci. His art blended profound meaning with beauty.
Jesus and his disciples are depicted in his painting “The Last Supper.” It conveys drama and emotion. The composition is strong and well-balanced.
“Mona Lisa” is another masterpiece. Her gaze follows the observer, and her smile is enigmatic. The realism and attention to detail in the painting are highly regarded.
Leonardo da Vinci researched anatomy, light, and shadow. He was able to paint realistic figures thanks to these studies. People’s perceptions of painting were altered by his work.
Scientific Observations

Leonardo da Vinci was more than just an artist. He was a scientist as well. He did extensive research on the human body.
He studied anatomy by dissecting corpses. He accurately and meticulously depicts muscles and organs in his drawings. They aided scientists and physicians.
He also researched the movement of water, plants, and animals. Leonardo da Vinci recorded his observations in notebooks. Sketches and ideas abound in his notes.
He applied the scientific method. He experimented with concepts and documented outcomes. He was ahead of his time.
Leonardo da Vinci: Engineering and Inventions

Leonardo da Vinci created a lot of machines. Some were constructed centuries later. He pictured robots, tanks, and flying machines.
He drew parachutes and helicopters. Bird flight served as the basis for these. Leonardo da Vinci thought that people could fly.
He designed water systems and bridges. His concepts made cities better. Later engineering projects made use of some of his designs.
His inventions weren’t all successful. But he had a limitless imagination. Leonardo da Vinci demonstrated how innovation propels advancement.
Anatomy and Human Body Studies
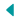
The human body captivated Leonardo da Vinci. He examined its motion and operation. Every muscle and bone was depicted in his drawings.
He dissected more than thirty bodies. He gained profound understanding as a result. Among his sketches is the well-known “Vitruvian Man.”
The human proportions in this drawing are ideal. It blends science and art. According to Leonardo da Vinci, the body reflects the natural world.
His work was used by artists and doctors. Both fields benefited from his studies. Even contemporary scientists were astounded by his accuracy.
Leonardo da Vinci: Architecture and Design
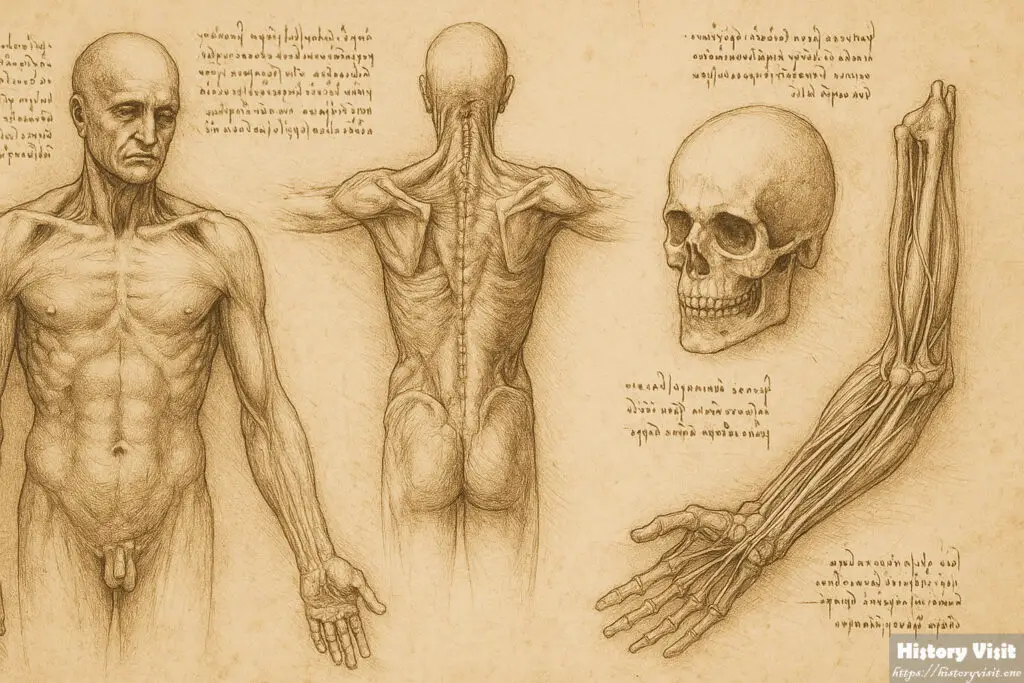
In addition, Leonardo da Vinci studied architecture. He designed cities, fortifications, and structures. He was ahead of his time with his designs.
He blended beauty and utility. His structures were elegantly shaped and robust. Harmony was important to Leonardo da Vinci.
He created perfect cities. Waste and clean water systems were among them. His goal was to make people’s lives better.
His ideas influenced others, but only a small number of his buildings were constructed. His visionary thinking is evident in his notebooks.
Leonardo da Vinci: Philosophy and Thought
Leonardo da Vinci was a thinker. He inquired about everything. He looked to nature for truth.
Learning, in his opinion, never ends. Until the end of his life, he continued to study. Thousands of pages were written by Leonardo da Vinci.
He thought there was a connection between science and art. They both traveled around the globe. The Renaissance was influenced by this notion.
Many others were inspired by his philosophy. He promoted observation and curiosity. Future thinkers looked up to Leonardo da Vinci.
Later Life and Legacy

Leonardo da Vinci relocated to France in his later years. He was employed by King Francis I. He brought his paintings and notebooks.
He kept studying and sketching. He continued to be active until 1519, when he passed away. At age 67, Leonardo da Vinci passed away.
He left behind a vast legacy. The greatest museums in the world have his artwork on display. Experts and students alike study his ideas.
Leonardo da Vinci made contributions to numerous fields. He altered our perspective on the world. His brilliance is still an inspiration.
Influence on Modern Science and Art
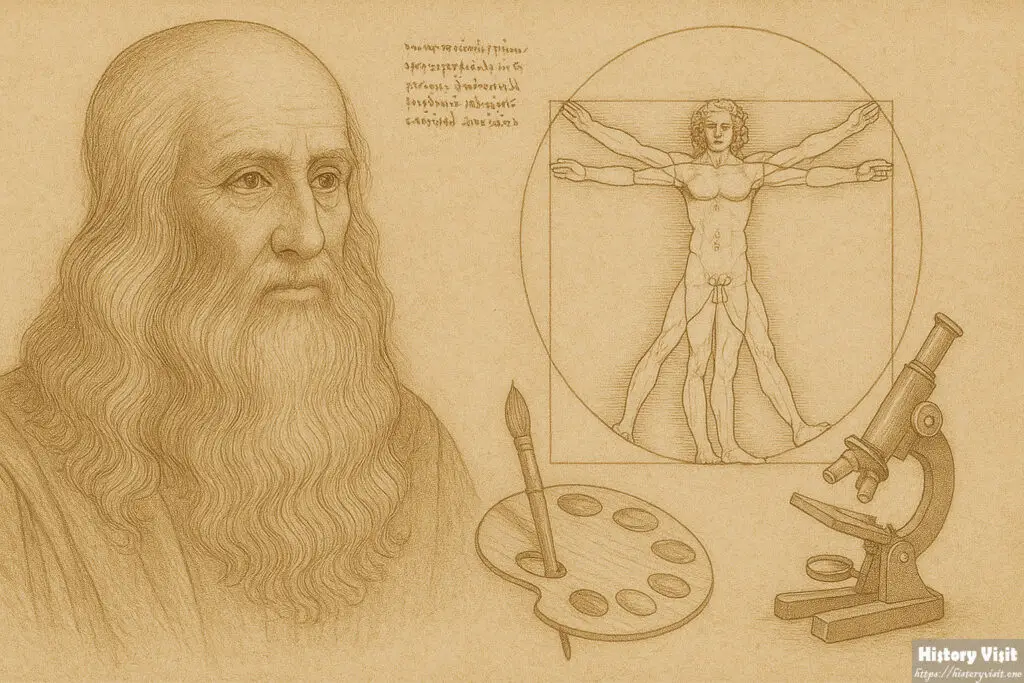
The impact of Leonardo da Vinci is still felt today. His methods are studied by artists. His curiosity is admired by scientists.
His anatomy drawings serve as a teaching tool for medical students. His mechanical designs are investigated by engineers. Numerous subjects were shaped by Leonardo da Vinci.
Translations of his notebooks have been distributed. They provide a window into his thoughts. New technology is based on his concepts.
He made the connection between science and art. This method is currently widely used. Leonardo da Vinci demonstrated the importance of interdisciplinary thinking.
Conclusion
Leonardo da Vinci was not just a superb painter. He was a thorough thinker. He looked everywhere for truth.
The world was altered by his work. His artwork moved people. Knowledge was enhanced by his science.
Leonardo da Vinci is still regarded as a genius today. He motivates thinkers, builders, and dreamers. His tale endures forever.