The Gothic Marvel: Notre-Dame Cathedral of Paris

Introduction
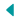
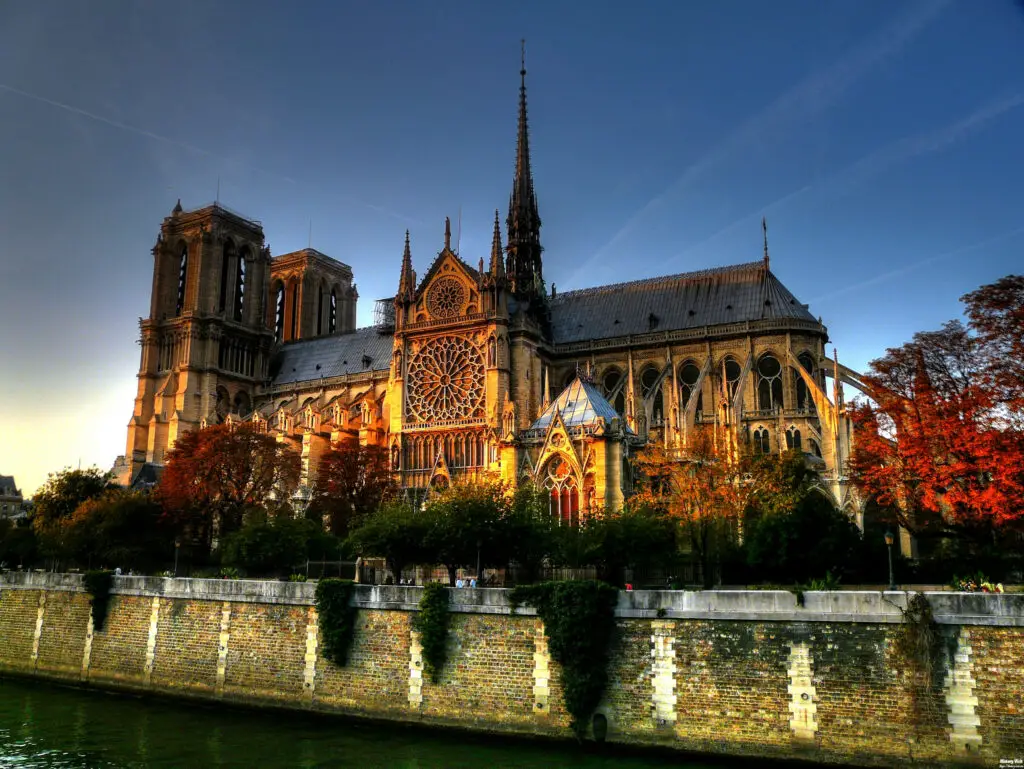
Notre-Dame Cathedral, an iconic symbol of Paris, stands as a testament to the grandeur and intricacy of Gothic architecture. Situated on the Île de la Cité in the heart of the French capital, this magnificent cathedral has witnessed centuries of history, becoming an enduring emblem of cultural and architectural achievement. As one of the most visited landmarks in the world, Notre-Dame attracts millions of visitors each year, eager to experience its stunning beauty and historical significance.
The construction of Notre-Dame began in the 12th century and took nearly two centuries to complete. Its builders harnessed the principles of Gothic architecture to create a structure that would not only inspire awe but also represent the spiritual aspirations of the time. The cathedral’s towering spires, intricate sculptures, and luminous stained glass windows are hallmarks of this architectural style, which sought to transcend the earthly realm and reach towards the heavens.
Notre-Dame’s importance extends beyond its architectural brilliance. It has played a central role in French history, serving as the site for royal coronations, state funerals, and other significant events. Despite the challenges it has faced, including the devastating fire in 2019, Notre-Dame remains a symbol of resilience and faith, continuing to captivate and inspire people from around the world.
Historical Background
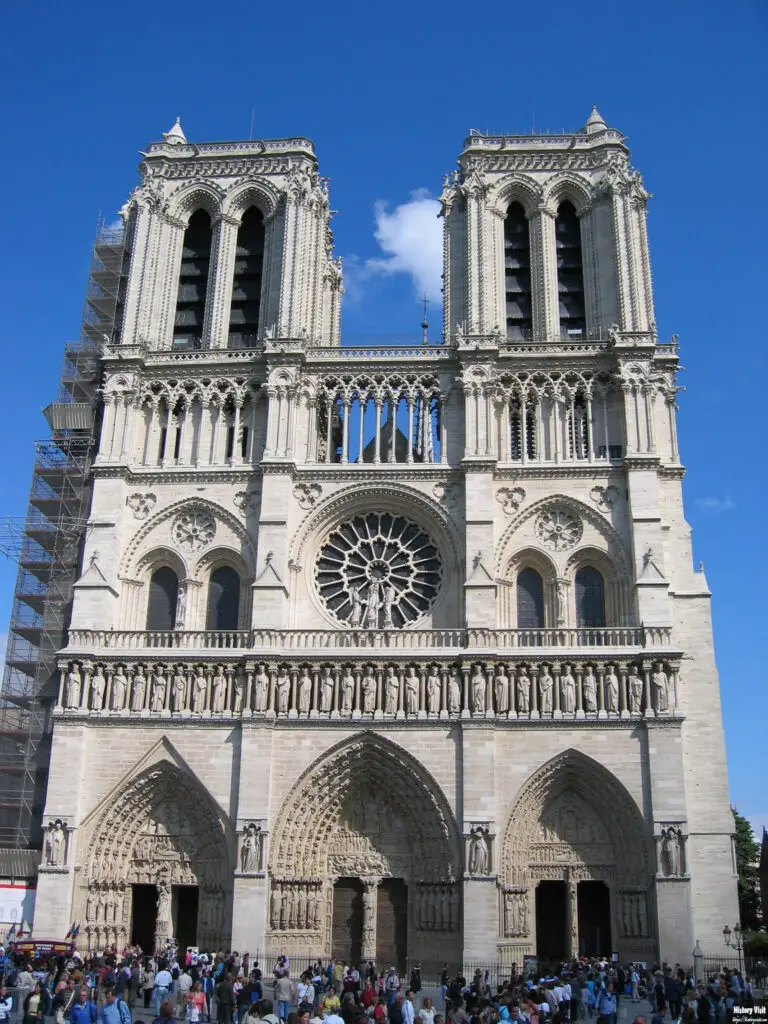

The construction of Notre-Dame Cathedral began in 1163, under the auspices of Bishop Maurice de Sully. The project aimed to create a grandiose place of worship befitting the growing importance of Paris as a cultural and political center. Over the next two centuries, various architects and craftsmen contributed to the cathedral’s construction, each adding their unique touches to the evolving design. The cathedral was finally completed in 1345, marking the culmination of nearly 200 years of architectural innovation and artistic achievement.
Throughout its history, Notre-Dame has been at the heart of significant events in France. It was the site of the coronation of Henry VI of England in 1431 during the Hundred Years’ War and the crowning of Napoleon Bonaparte as Emperor of the French in 1804. The cathedral also played a pivotal role during the French Revolution, when many of its religious artifacts were destroyed, and it was briefly converted into a Temple of Reason.
Notre-Dame’s historical significance is also reflected in its status as a UNESCO World Heritage site, designated in 1991. This recognition underscores the cathedral’s importance not only as an architectural masterpiece but also as a symbol of the cultural and historical heritage of France and Europe. Its enduring legacy continues to be celebrated and preserved for future generations.
Architectural Features
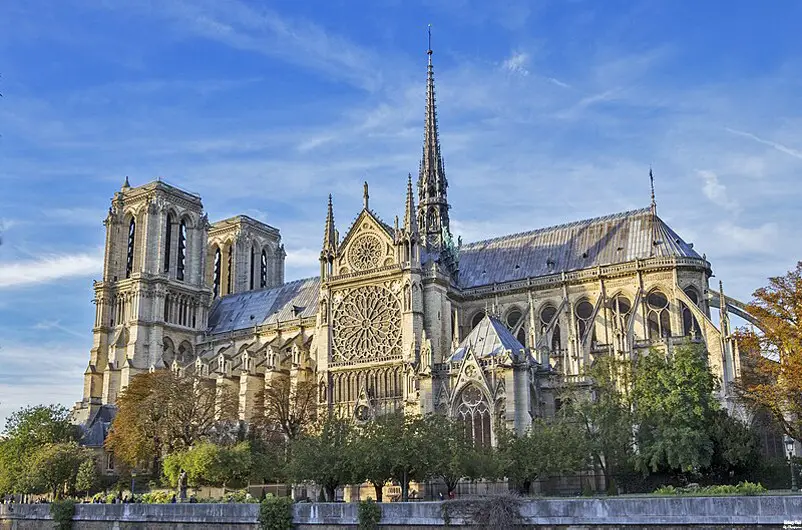

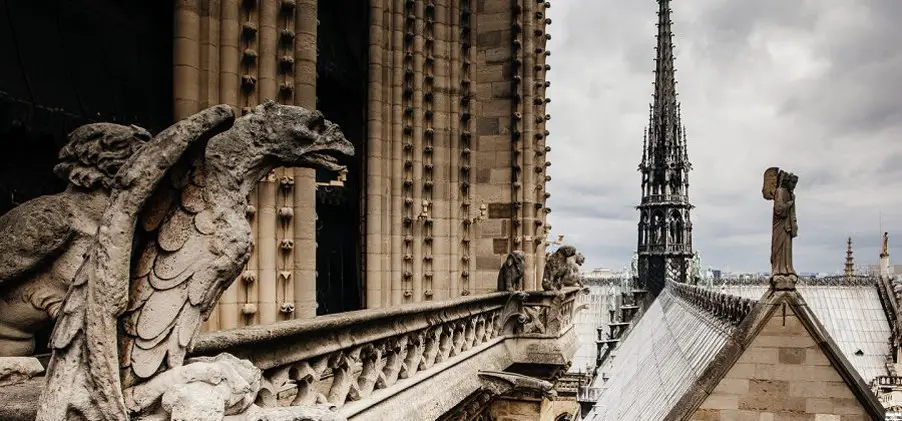
The exterior design of Notre-Dame Cathedral is a stunning example of Gothic architectural principles. Its facade is adorned with an array of sculptures and statues, including the famous gargoyles that serve both decorative and functional purposes. These stone figures, often depicting fantastical creatures, act as water spouts to divert rainwater away from the building, protecting its walls from erosion. The cathedral’s iconic flying buttresses, which were added in the 13th century, provide additional support to the soaring walls, allowing for the inclusion of large stained glass windows.
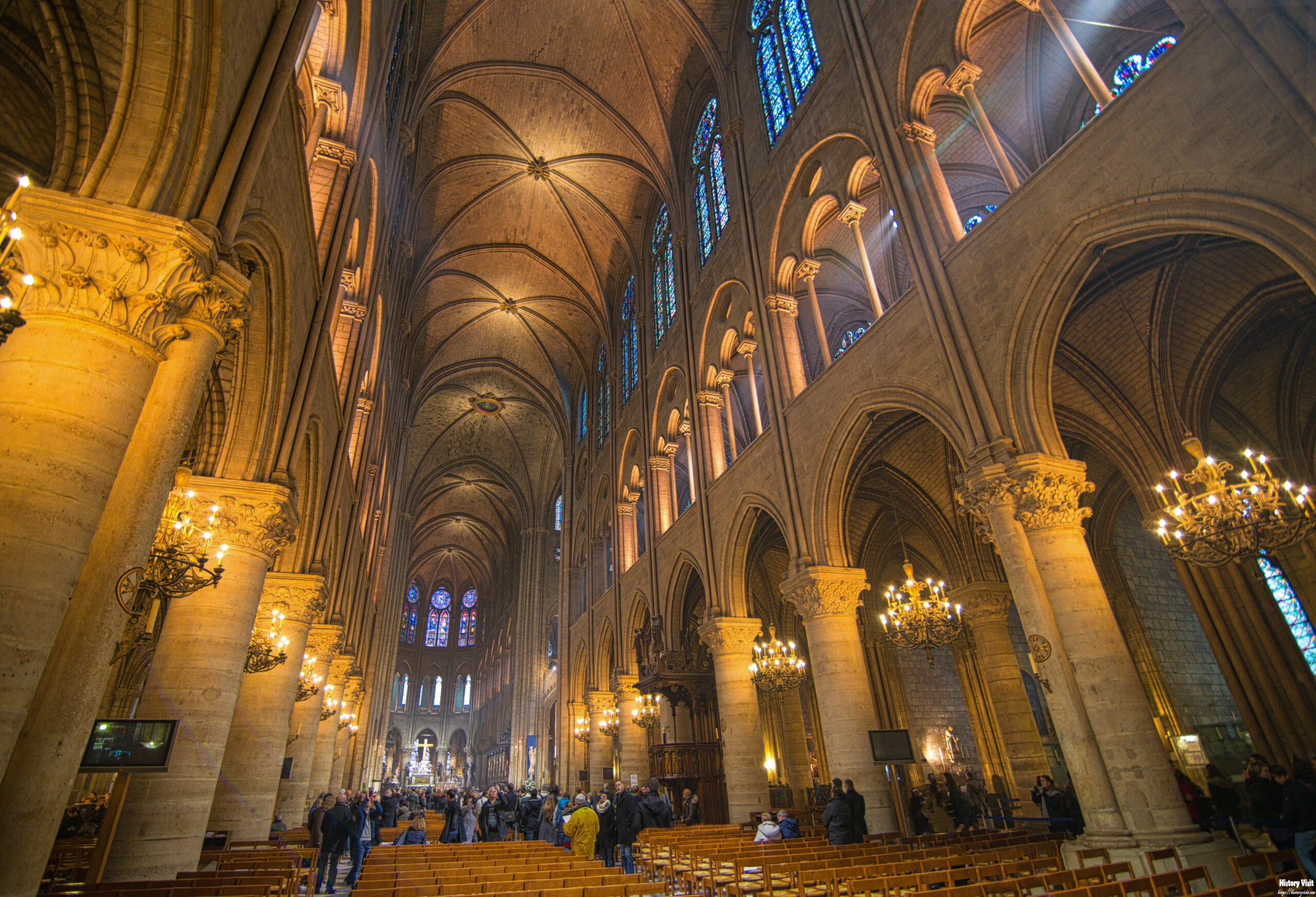

Inside, the cathedral’s ribbed vaults create a sense of height and lightness, characteristic of Gothic architecture. The nave, with its impressive height and narrow design, draws the eye upward, evoking a sense of spiritual ascent. The altar and choir, richly decorated with intricate carvings and sculptures, form the focal point of the interior, reflecting the cathedral’s primary function as a place of worship.
One of the most striking features of Notre-Dame is its stained glass windows, particularly the three rose windows. These circular windows, located on the west, north, and south facades, are masterpieces of Gothic art, depicting scenes from the Bible and the lives of saints. The interplay of light through the colored glass creates a mesmerizing effect, transforming the interior into a kaleidoscope of colors and enhancing the spiritual atmosphere of the cathedral.
Gothic Elements
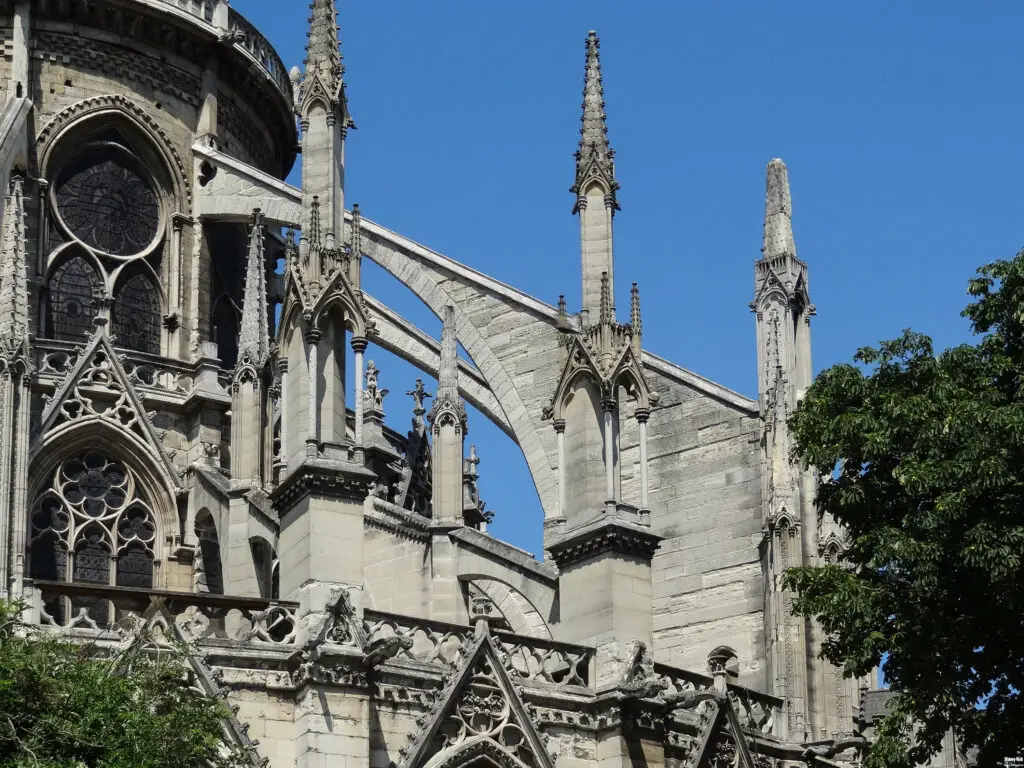

Gothic architecture, which flourished in Europe from the 12th to the 16th centuries, is characterized by its emphasis on height, light, and intricate ornamentation. Notre-Dame Cathedral exemplifies these principles through its innovative use of structural elements and decorative features. The pointed arches, ribbed vaults, and flying buttresses not only provide structural support but also create a sense of verticality and openness, drawing the eye upward and allowing light to flood the interior.
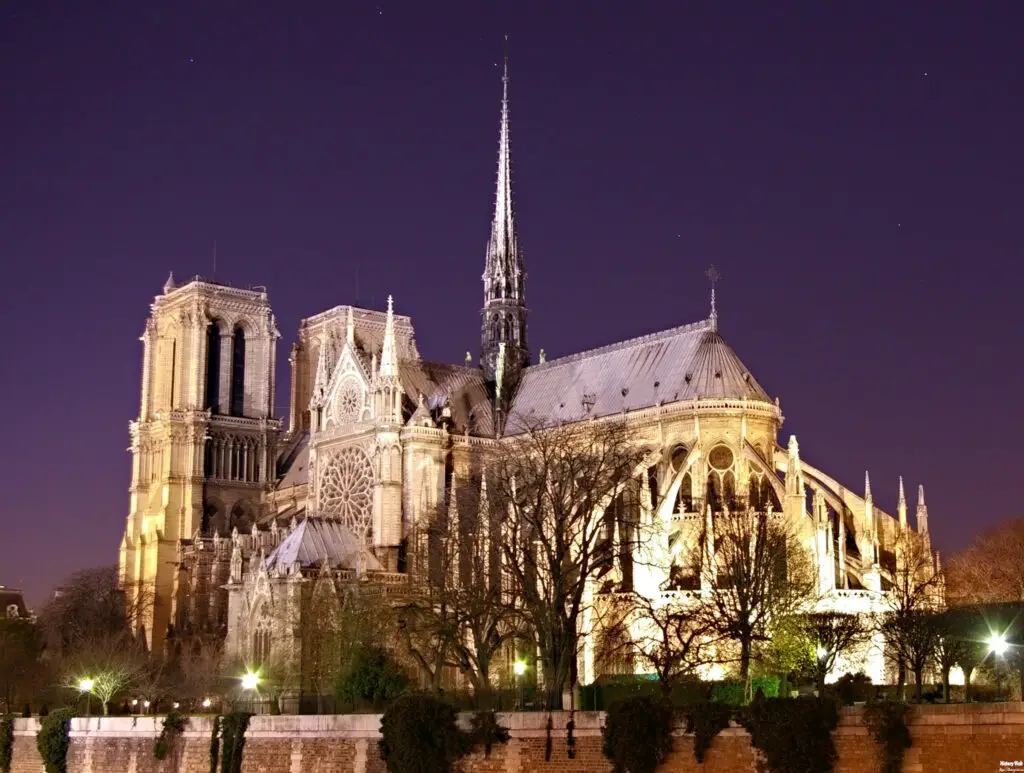

The cathedral’s detailed ornamentation, from the sculpted portals to the intricate tracery of the windows, showcases the Gothic fascination with decoration and symbolism. Every element of the cathedral’s design serves a dual purpose: to enhance the beauty of the structure and to convey religious and moral messages. The sculptures and carvings depict scenes from the Bible, the lives of saints, and allegorical figures, serving as visual sermons for the faithful.
Notre-Dame’s use of light is another hallmark of Gothic architecture. The expansive stained glass windows, particularly the rose windows, fill the interior with a vibrant play of colors, creating a sense of ethereal beauty. This use of light and color was intended to inspire awe and reverence, elevating the spiritual experience of those who entered the cathedral. The careful balance of light and shadow, achieved through the architectural design, enhances the sense of divine presence within the sacred space.
Art and Iconography
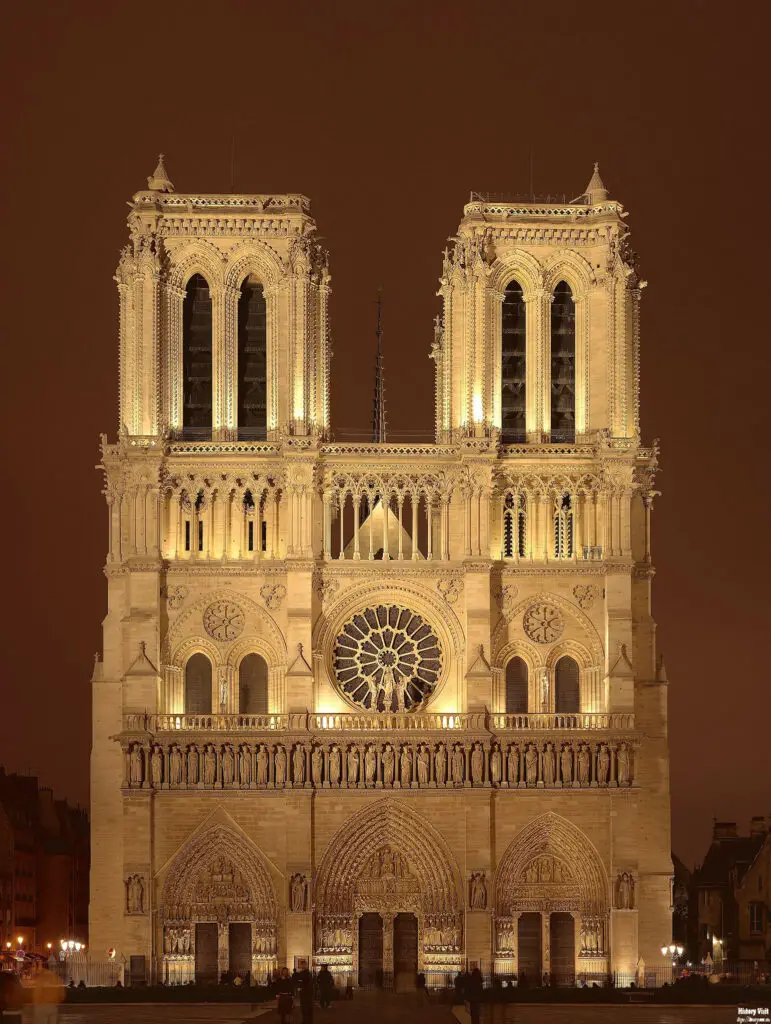

Notre-Dame Cathedral is not only an architectural masterpiece but also a repository of some of the finest examples of Gothic art and iconography. The cathedral’s facade is adorned with numerous sculptures, including the famous Gallery of Kings, which features 28 statues representing the kings of Judah. These sculptures, along with the detailed carvings on the portals, depict biblical scenes and moral allegories, serving as visual storytelling for the medieval faithful.
Inside the cathedral, the artistic richness continues with an array of sculptures, paintings, and stained glass windows. The choir screen, adorned with intricate carvings depicting scenes from the life of Christ, is a notable example of Gothic artistry. The statues of saints and angels, positioned throughout the interior, add to the cathedral’s spiritual ambiance, reminding visitors of the sacred significance of the space.
The stained glass windows of Notre-Dame are among its most celebrated features. The three rose windows, each measuring over 10 meters in diameter, are masterpieces of Gothic art. The west rose window, the oldest of the three, depicts the Last Judgment, while the north and south rose windows illustrate scenes from the Old and New Testaments, respectively. These windows, with their intricate designs and vibrant colors, not only enhance the beauty of the cathedral but also convey profound religious messages, inviting contemplation and reflection.
Cultural and Religious Significance

Notre-Dame Cathedral has long been a central hub of religious activity in Paris. As the seat of the Archbishop of Paris, it has hosted countless religious ceremonies, from daily masses to significant events such as royal coronations and state funerals. The cathedral’s role as a place of worship and pilgrimage has been integral to its identity, attracting believers and visitors from around the world.
Beyond its religious function, Notre-Dame has also played a prominent role in literature and the arts. Victor Hugo’s novel “The Hunchback of Notre-Dame,” published in 1831, brought renewed attention to the cathedral, highlighting its architectural beauty and historical significance. Hugo’s portrayal of the cathedral as a central character in the story helped to spark a movement to preserve and restore Gothic architecture in France, leading to major restoration efforts in the 19th century.
The cathedral has also been the site of numerous significant events in French history. In addition to royal coronations, Notre-Dame has witnessed the liberation of Paris in 1944, celebrated with a Te Deum mass attended by General Charles de Gaulle. The cathedral’s bells rang out in celebration, symbolizing hope and resilience in times of adversity. This rich history of cultural and religious significance underscores Notre-Dame’s enduring importance as a symbol of French heritage and identity.
The 2019 Fire and Restoration Efforts
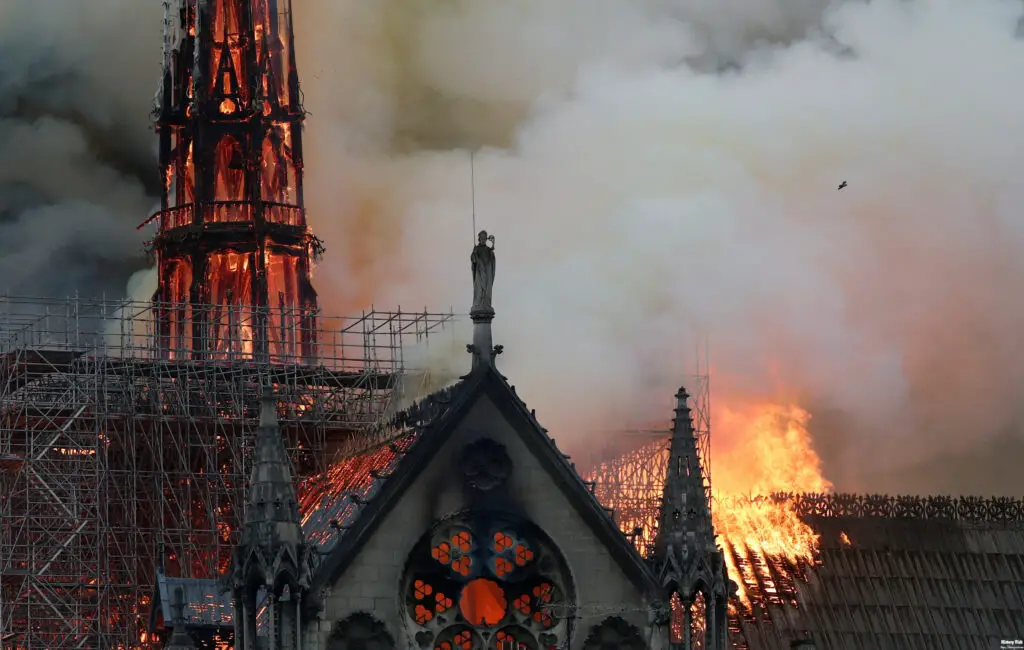

On April 15, 2019, a devastating fire broke out at Notre-Dame Cathedral, causing extensive damage to the roof and spire. The fire, which burned for several hours, led to the collapse of the spire and the destruction of the wooden roof structure, known as “the forest” due to its intricate framework of ancient timbers. The world watched in shock and sorrow as firefighters battled to save the iconic landmark, ultimately managing to preserve the main structure and many of its invaluable artifacts.
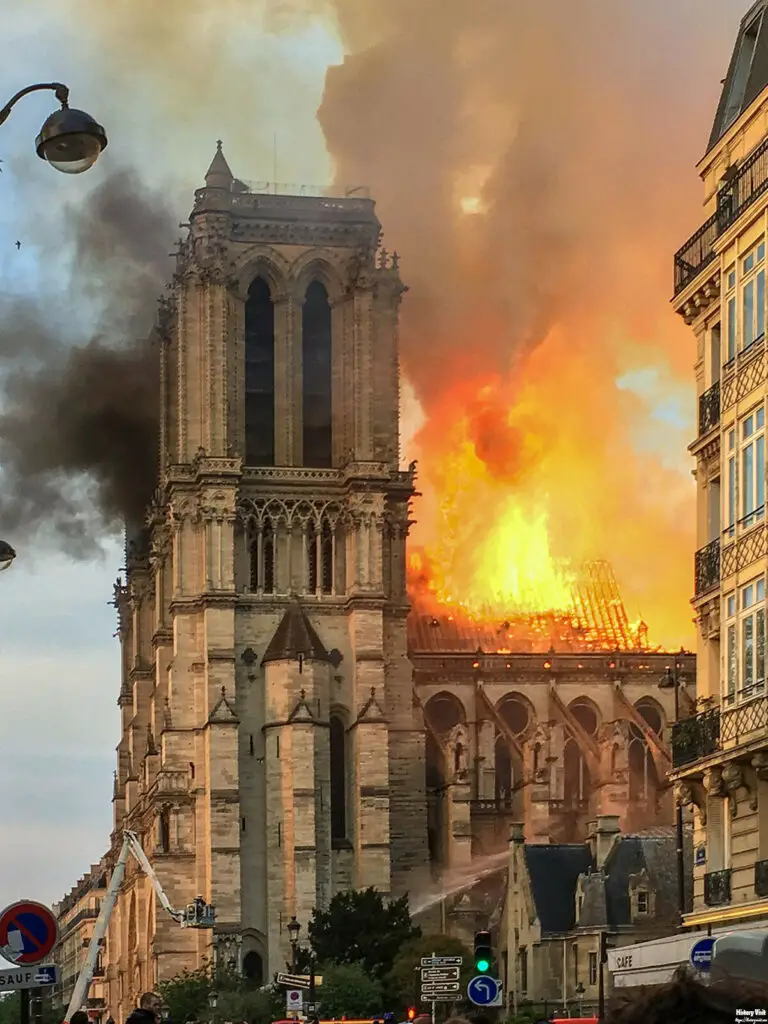

In the aftermath of the fire, a massive restoration effort was launched to rebuild and restore Notre-Dame. French President Emmanuel Macron pledged to restore the cathedral within five years, a commitment that has mobilized significant financial and technical resources from around the world. The restoration project aims not only to repair the damage but also to ensure that the cathedral is preserved for future generations. This includes painstakingly reconstructing the roof and spire, using traditional materials and techniques to maintain historical accuracy.
The restoration efforts have also provided an opportunity to modernize and improve certain aspects of the cathedral, such as its fire safety measures. Advances in technology are being incorporated to enhance the building’s resilience while preserving its historical integrity. The global outpouring of support and the dedication of the restoration teams underscore the profound significance of Notre-Dame as a cultural and spiritual treasure.
Visitor Experience
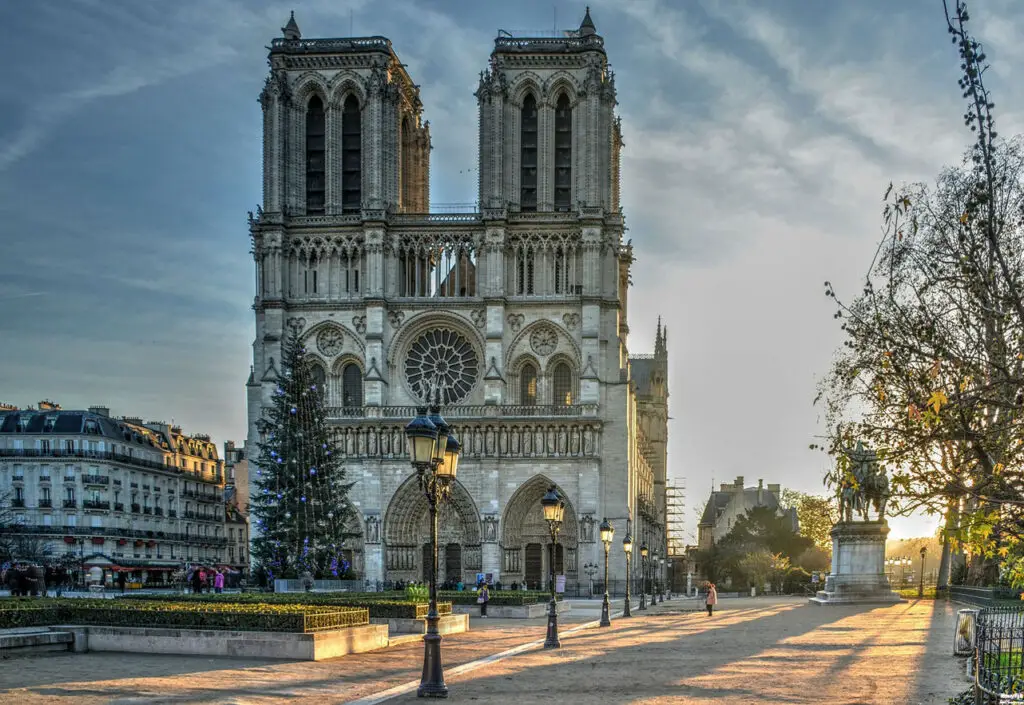

Visiting Notre-Dame Cathedral is a profound experience that offers a glimpse into the grandeur of Gothic architecture and the rich history of Paris. Upon entering the cathedral, visitors are immediately struck by the soaring height of the nave and the intricate details of the interior. The play of light through the stained glass windows creates a mesmerizing atmosphere, enhancing the sense of awe and reverence.
Key areas to explore include the west facade, with its detailed sculptures and portals, and the interior, with its magnificent altar, choir, and chapels. The north and south rose windows are particularly noteworthy, offering stunning examples of medieval stained glass artistry. Visitors can also climb the towers for a panoramic view of Paris and a close-up look at the famous gargoyles and chimeras that adorn the cathedral’s exterior.
For those planning a visit, it is advisable to arrive early to avoid long lines and to take advantage of guided tours that provide deeper insights into the history and architecture of Notre-Dame. The cathedral’s proximity to other notable landmarks, such as the Sainte-Chapelle and the Conciergerie, makes it a central point for exploring the historical heart of Paris. Despite the ongoing restoration efforts, Notre-Dame remains open to visitors, continuing to offer a unique and enriching experience.
Conclusion
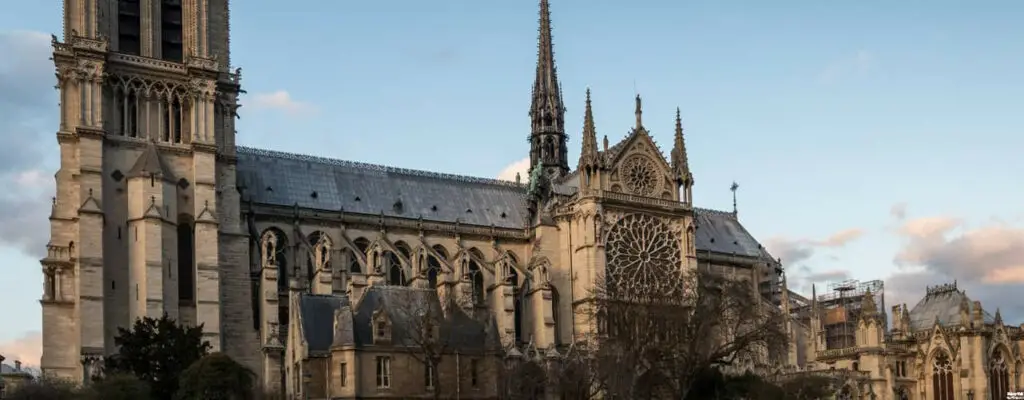

Notre-Dame Cathedral stands as a timeless testament to the ingenuity and artistic vision of the Gothic architects who conceived it. Its towering spires, intricate sculptures, and luminous stained glass windows continue to inspire awe and reverence, drawing millions of visitors each year. The cathedral’s rich history, from its role in royal ceremonies to its influence on literature and the arts, underscores its significance as a cultural and spiritual icon.
The devastating fire of 2019 was a poignant reminder of the cathedral’s fragility and the importance of preserving our shared heritage. The ongoing restoration efforts reflect a global commitment to safeguarding this architectural masterpiece for future generations. As Notre-Dame rises from the ashes, it symbolizes not only resilience and renewal but also the enduring power of faith and creativity.
In the heart of Paris, Notre-Dame Cathedral remains a beacon of Gothic splendor, a place where history, art, and spirituality converge. Its enduring legacy continues to captivate and inspire, reminding us of the profound connection between the past and the present. As we look to the future, Notre-Dame will undoubtedly remain a cherished symbol of human achievement and a testament to the enduring beauty of Gothic architecture.