Renaissance Artwork: A Journey Through Beauty and Innovation

Introduction
Renaissance artwork marks one of history’s greatest artistic revolutions. This movement began in the 14th century. It inspired a new way of thinking about art and human potential. Renaissance artwork brought life, detail, and emotion into painting, sculpture, and architecture. Artists explored nature, the human body, and perspective with unmatched skill.
The Renaissance began in Italy before spreading across Europe. Florence, Rome, and Venice became art centers. Wealthy patrons supported artists, allowing them to create timeless masterpieces. The Medici family, for example, helped fund many famous works. Renaissance artwork reflected both beauty and intellectual growth. It celebrated the balance between science, art, and humanism.
This period reshaped the history of art. It blended classical ideals with innovative techniques. The work of great masters still influences artists today. Studying renaissance artwork helps us understand the link between creativity and cultural change.
Origins of Renaissance Artwork
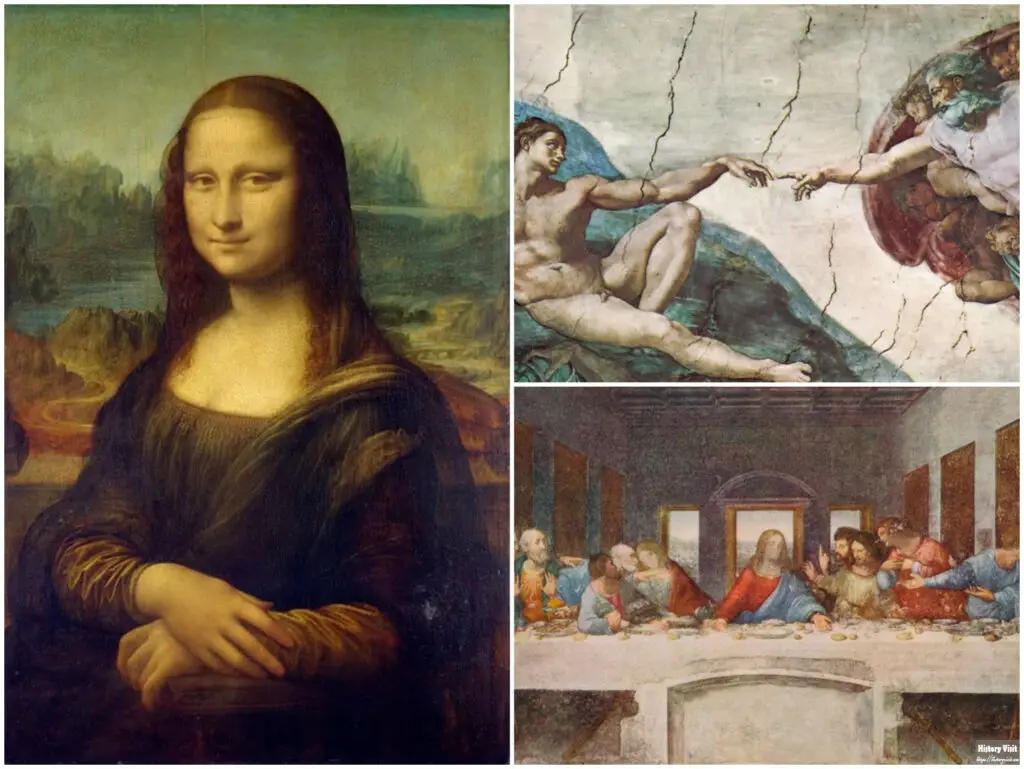
Renaissance artwork emerged after the Middle Ages. The period saw a renewed interest in ancient Greek and Roman culture. Artists studied old sculptures, manuscripts, and architectural ruins. They sought to bring back classical harmony and proportion.
The Black Death had devastated Europe. Society was rebuilding, and people sought beauty and hope. Renaissance artwork became a reflection of human optimism. Artists used their skills to express the human experience in new ways.
In Italy, city-states competed for cultural glory. Florence especially became a hub for innovation. Guilds and wealthy families funded painters, sculptors, and architects. Public spaces began displaying grand works of art.
The early phase, called the Proto-Renaissance, laid the foundation. Artists like Giotto introduced realistic figures and depth. These changes prepared the way for the High Renaissance.
Key Characteristics of Renaissance Artwork

Renaissance artwork had distinct features. Realism became a major focus. Artists studied anatomy to depict the human body accurately. They observed nature to create lifelike landscapes.
Perspective transformed painting. Linear perspective gave depth to flat surfaces. This made scenes look three-dimensional. Atmospheric perspective added realism by showing distant objects as lighter and hazier.
Chiaroscuro was another key technique. It used light and shadow to create form. This method made figures appear more solid and natural.
Symbolism was common in renaissance artwork. Religious scenes often included hidden meanings. Everyday objects carried moral or spiritual significance.
Famous Artists of Renaissance Artwork
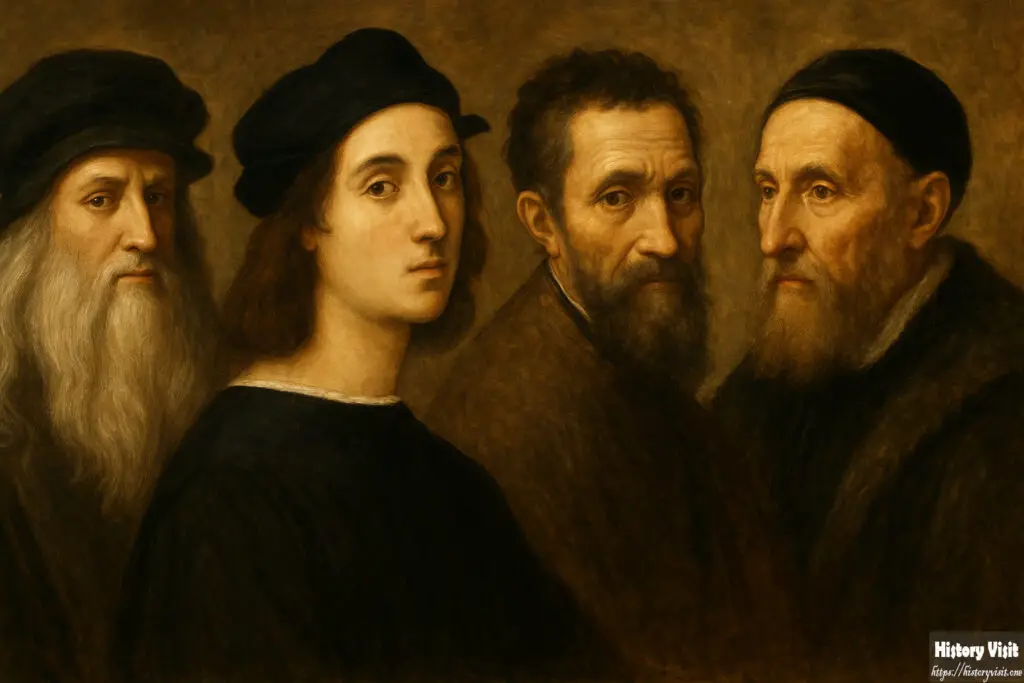

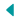
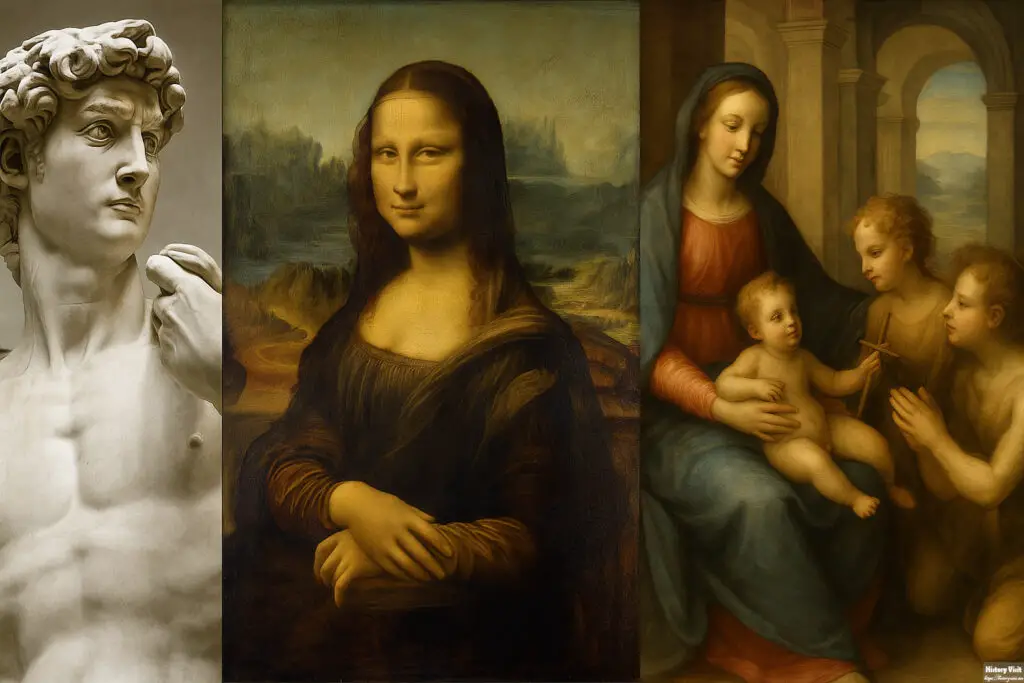
The Renaissance produced legendary artists. Leonardo da Vinci was a master of many disciplines. His works, like The Last Supper and Mona Lisa, remain iconic. He studied anatomy, engineering, and nature to enhance his art.
Michelangelo excelled in sculpture, painting, and architecture. His David and the Sistine Chapel ceiling are masterpieces. His work displayed unmatched technical skill and emotional depth.
Raphael was known for grace and harmony. His frescoes in the Vatican are celebrated worldwide. He blended classical ideals with warm human expression.
Titian brought vibrant color to renaissance artwork. His portraits and mythological scenes influenced future generations of painters.
Themes in Renaissance Artwork
Renaissance artwork often reflected humanism. This philosophy valued human potential and achievements. Artists portrayed figures as individuals with emotions and personality.
Religious themes remained important. Biblical stories were given realistic settings. Saints and angels were shown as relatable human beings.
Mythology also inspired many works. Scenes from ancient myths symbolized moral lessons or human desires. These artworks often blended fantasy with natural beauty.
Portraits became popular among the wealthy. They wanted to display their power and sophistication. Artists used symbolism to reflect the subject’s virtues and status.
Renaissance Artwork in Sculpture
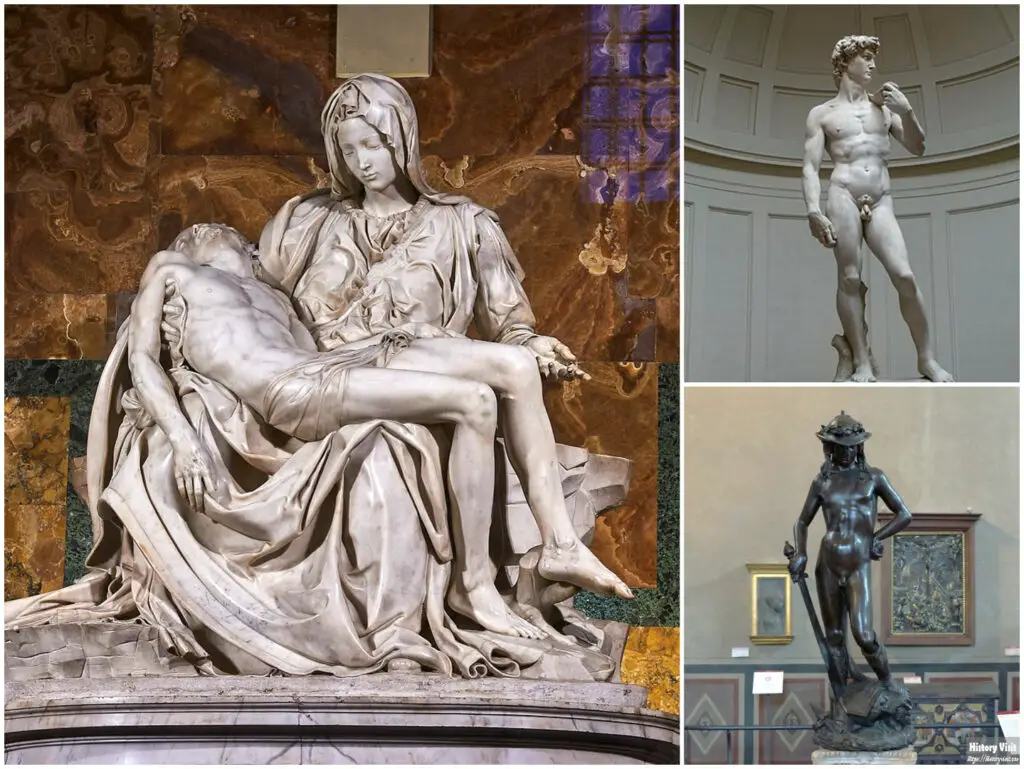

Sculpture saw a major revival during the Renaissance. Artists studied ancient statues for inspiration. They aimed to create works that combined ideal beauty with realistic detail.
Donatello was a pioneer. His bronze David showed natural movement and youthful confidence. This was a bold step away from medieval stiffness.
Michelangelo’s sculptures captured human strength and vulnerability. His marble Pietà and David reveal deep understanding of anatomy. Each detail was carved with precision and emotion.
Renaissance sculpture often decorated churches and public squares. These works were both art and political symbols. They reflected civic pride and religious devotion.
Architecture in Renaissance Artwork
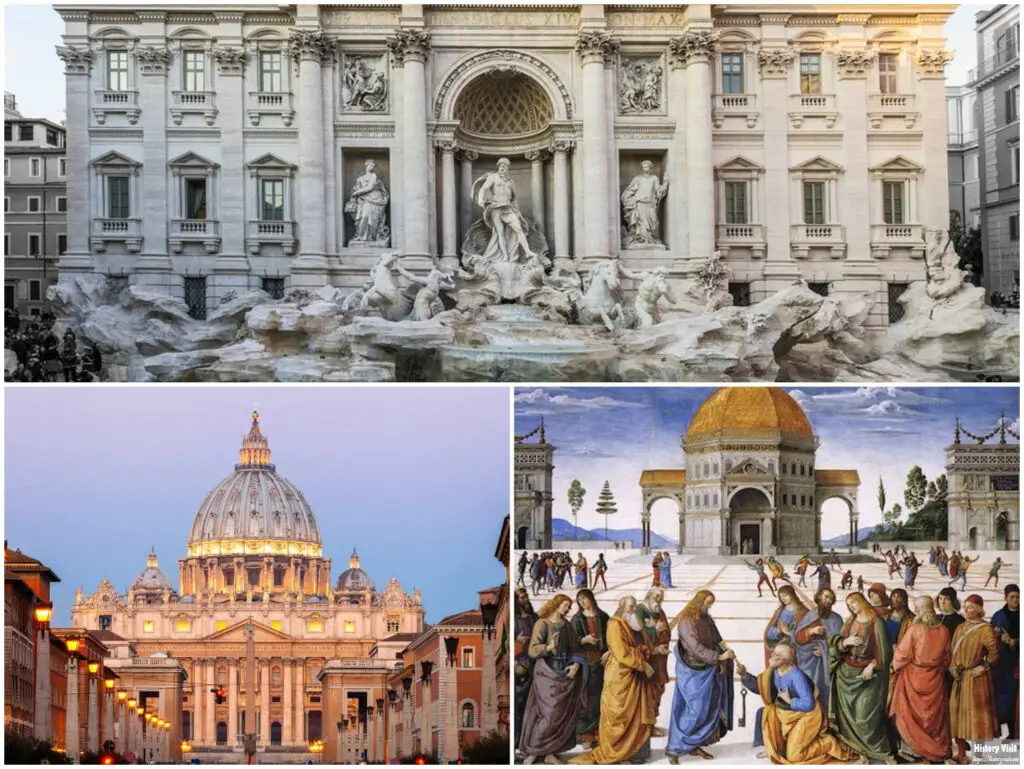

Architecture became a central part of renaissance artwork. Designers looked to classical Rome for ideas. They used columns, domes, and arches in new ways.
Filippo Brunelleschi revolutionized architecture. He designed the dome of Florence Cathedral. His work combined engineering skill with beauty.
Leon Battista Alberti wrote treatises on architecture. He believed buildings should reflect order and harmony. His designs influenced architects across Europe.
Renaissance palaces and churches showed balance and proportion. Decorative details, frescoes, and sculptures often enhanced the architecture.
Renaissance Artwork Across Europe
While Italy led the movement, renaissance artwork spread quickly. In France, King Francis I invited Italian artists to his court. Leonardo da Vinci spent his final years there.
In the Netherlands, artists like Jan van Eyck perfected oil painting. Their works were rich in detail and texture.
Germany saw Albrecht Dürer blending Italian techniques with Northern traditions. His engravings and paintings showed both precision and imagination.
England’s Renaissance art often focused on portraiture. Hans Holbein the Younger created striking images of the Tudor court.
The Legacy of Renaissance Artwork
Renaissance artwork changed the course of art history. Its influence is visible in later movements like Baroque and Neoclassicism. Artists learned to merge science, observation, and creativity.
Art academies grew from Renaissance traditions. They taught anatomy, perspective, and classical studies. These methods shaped Western art education for centuries.
Public museums now display many Renaissance works. People travel worldwide to see them. Their beauty and skill continue to inspire.
Modern artists still study Renaissance masters. The movement’s ideals remain a foundation for creativity today.
Conclusion
Renaissance artwork was more than an art style. It was a reflection of a cultural rebirth. Artists combined ancient wisdom with new discoveries. Their works captured human beauty, emotion, and intellect.
The movement reshaped painting, sculpture, and architecture. It celebrated the human spirit and the wonders of the natural world. Every masterpiece told a story of ambition and innovation.
Today, renaissance artwork still speaks across centuries. Its timeless beauty and ideas remain a guide for art lovers everywhere. The Renaissance proved that creativity can change the world