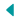
Guardians of an Empire: The Terracotta Army of Xi’an, China

Introduction
The Terracotta Army, one of the most remarkable archaeological discoveries of the 20th century, stands as a testament to the power and ingenuity of ancient China. Located in Xi’an, China, this vast collection of life-sized clay soldiers, chariots, and horses dates back to the reign of Qin Shi Huang, the first emperor of China, circa 210-209 BC. Discovered in 1974 by local farmers, the Terracotta Army has since captured the imagination of people worldwide, offering a glimpse into the ancient past and the grandeur of China’s imperial history.
The significance of the Terracotta Army extends beyond its sheer scale and craftsmanship. It provides invaluable insights into the military, artistic, and cultural achievements of the Qin Dynasty. Moreover, its discovery has revolutionized our understanding of ancient Chinese burial practices and beliefs about the afterlife. As one of the most iconic symbols of China’s rich cultural heritage, the Terracotta Army continues to inspire awe and fascination, drawing millions of visitors each year to marvel at its intricate detail and historical significance.
Historical Context
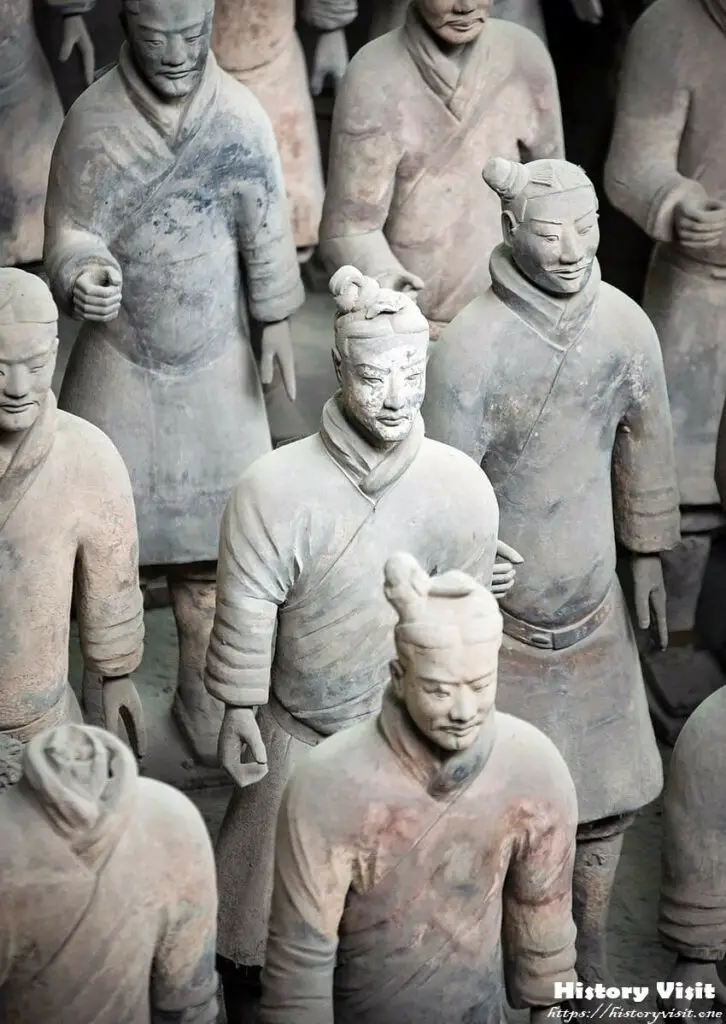

The construction of the Terracotta Army took place during the reign of Qin Shi Huang, who unified China and established the Qin Dynasty in 221 BC. Determined to maintain his power and control in the afterlife, Qin Shi Huang ordered the construction of a massive funerary complex, including the elaborate mausoleum guarded by the Terracotta Army. This vast project employed thousands of laborers and artisans over several decades, showcasing the emperor’s ambition and vision for his eternal legacy.
The Terracotta Army served a dual purpose in ancient Chinese society. On one hand, it functioned as a symbol of imperial might and military prowess, reflecting Qin Shi Huang’s desire to project strength both in life and death. Each meticulously crafted soldier, with its unique facial features and armor, represented a real member of the emperor’s army, ready to defend him in the afterlife. On the other hand, the army also served a religious and spiritual role, believed to accompany the emperor in his journey to the underworld and protect him from malevolent forces.
The discovery of the Terracotta Army in 1974 by a group of farmers digging a well in Xi’an, China, marked a turning point in our understanding of ancient Chinese history. Unearthed in three massive pits, the army consisted of thousands of clay soldiers, horses, and chariots arranged in battle formation. This remarkable find not only shed light on the military organization and technology of the Qin Dynasty but also raised intriguing questions about the emperor’s burial practices and the cultural beliefs of ancient China.
Discovery and Excavation
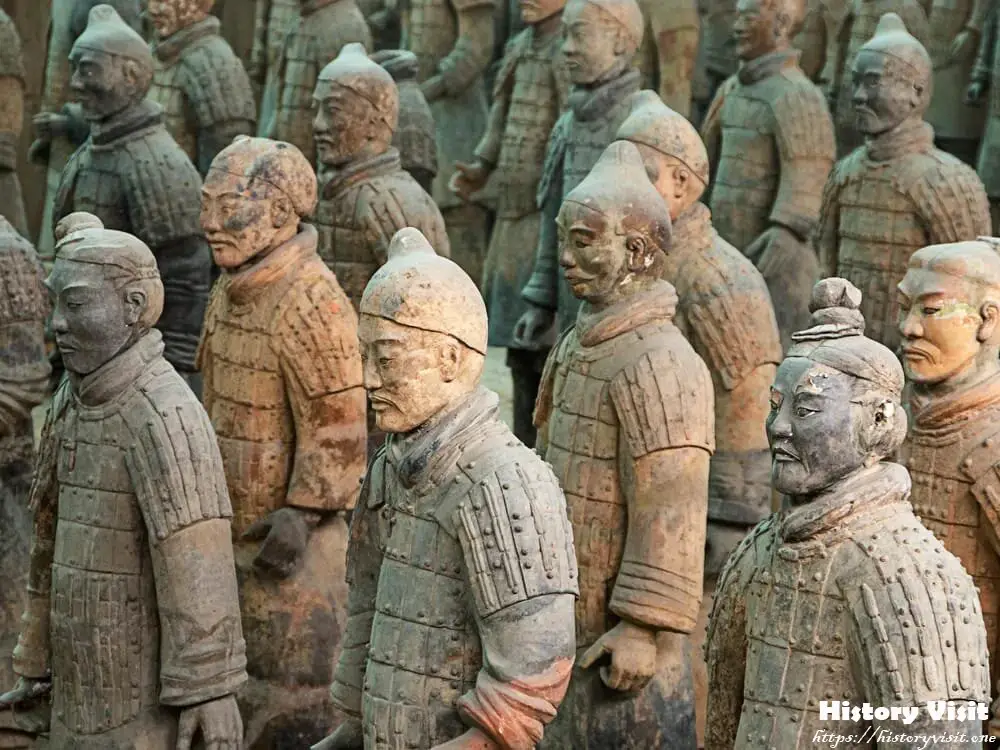

The discovery of the Terracotta Army in 1974 by a group of farmers digging a well in Xi’an, China, marked a turning point in our understanding of ancient Chinese history. Unearthed in three massive pits, the army consisted of thousands of clay soldiers, horses, and chariots arranged in battle formation. This remarkable find not only shed light on the military organization and technology of the Qin Dynasty but also raised intriguing questions about the emperor’s burial practices and the cultural beliefs of ancient China.
Archaeological excavations at the site have revealed the meticulous planning and craftsmanship that went into creating the Terracotta Army. Each soldier was individually sculpted with distinct facial features, hairstyles, and armor, reflecting the diversity of the Qin military. The scale of the project, spanning over several decades and involving thousands of laborers and artisans, underscores the importance of the emperor’s burial and his desire for an elaborate afterlife.
Conservation efforts have been ongoing since the discovery of the Terracotta Army to preserve this invaluable cultural heritage. The excavation site has been carefully managed to prevent further deterioration of the clay figures, while innovative techniques and technologies have been employed to stabilize and restore damaged sculptures. The preservation of the Terracotta Army not only ensures its continued study and appreciation but also honors the legacy of ancient China and its contributions to world civilization.
Composition and Detail
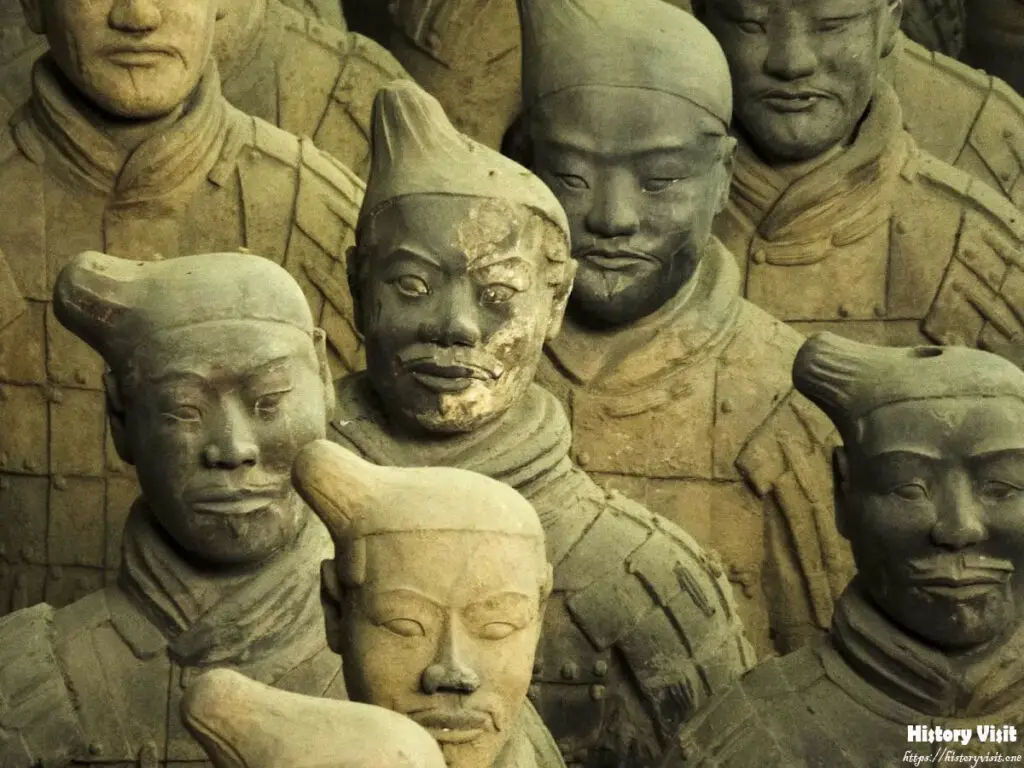

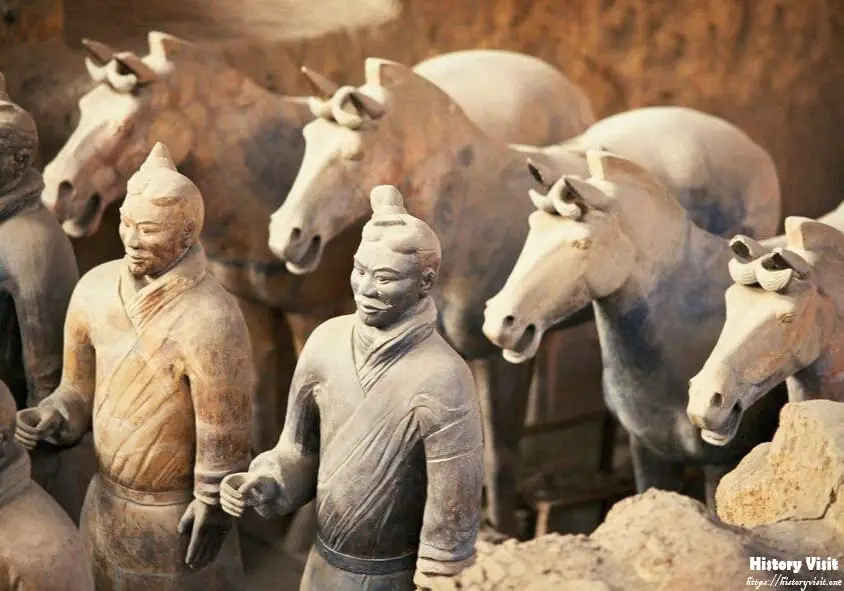
The Terracotta Army is composed of thousands of life-sized clay soldiers, each meticulously crafted with remarkable attention to detail. The soldiers vary in height, hairstyle, and facial features, reflecting the diversity of the Qin military. Archaeologists have identified different types of soldiers, including infantry, cavalry, archers, and charioteers, each with its own role and function in battle. This level of organization and specialization highlights the strategic sophistication of the Qin Dynasty’s military forces.
The individuality of each soldier in the Terracotta Army is a testament to the skill and artistry of the ancient artisans who created them. From the intricate patterns on their armor to the subtle expressions on their faces, every detail has been carefully rendered to evoke a sense of realism and personality. The soldiers stand in formation, ready for battle, their weapons at the ready and their expressions frozen in determination, capturing a moment in time preserved for eternity.
The diversity of the Terracotta Army extends beyond its soldiers to include chariots, horses, and other accompanying figures. Chariots, elaborately decorated with ornate designs and symbols of imperial authority, were essential components of ancient Chinese warfare, serving as command centers for generals and officers. The inclusion of chariots in the Terracotta Army reinforces its role as a representation of the emperor’s military might and his vision for eternal protection in the afterlife.
Interpretation and Symbolism
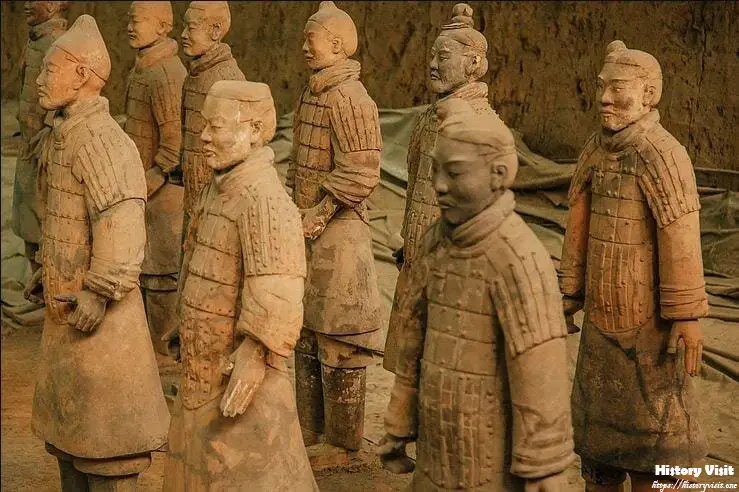

The purpose of the Terracotta Army extends beyond its role as a military force; it also holds deep symbolic significance in ancient Chinese culture and religion. Believed to accompany the emperor in his journey to the afterlife, the army served as his eternal guardians, protecting him from harm and ensuring his continued reign in the underworld. The meticulous construction and arrangement of the soldiers reflect the emperor’s desire for order and control, both in life and death.
The inclusion of weapons and armor in the Terracotta Army underscores its role as a symbol of power and authority. Each soldier is equipped with fully functional weapons, including swords, spears, and crossbows, emphasizing the military strength of the Qin Dynasty and its ability to defend the empire from external threats. The intricate details of the armor, adorned with symbols of rank and status, further reinforce the soldiers’ elite status and their importance in the emperor’s retinue.
The Terracotta Army also reflects the ancient Chinese belief in the afterlife and the importance of proper burial rituals. In Chinese culture, it was believed that the soul of the deceased required material possessions and spiritual guardians to ensure a safe passage to the afterlife. The construction of the Terracotta Army, with its thousands of soldiers and horses, was a manifestation of this belief, serving as a physical representation of the emperor’s authority and his continued presence in the world beyond.
Legacy and Impact
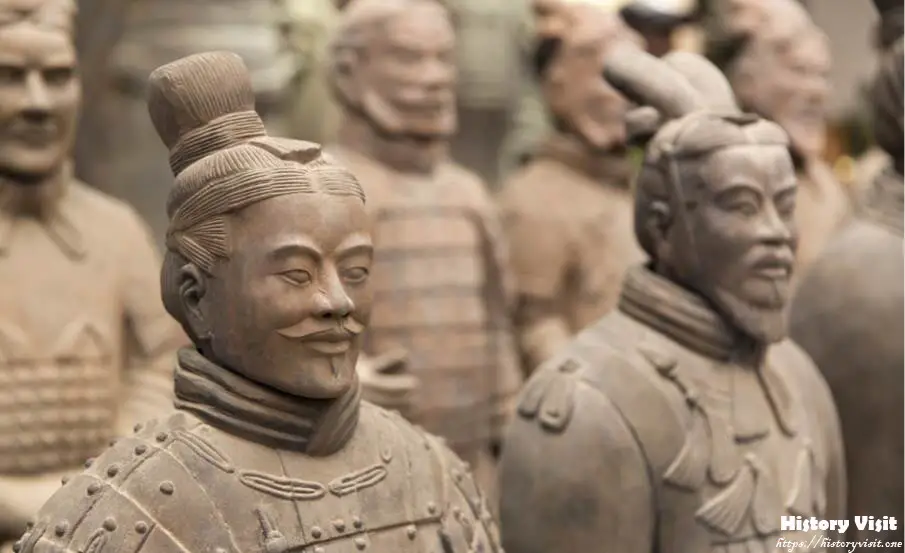

The legacy of the Terracotta Army extends beyond its historical significance to influence contemporary art, culture, and scholarship. Its iconic status as a symbol of China’s rich cultural heritage has made it a source of inspiration for artists, filmmakers, and writers around the world. The striking imagery of the army, with its ranks of silent warriors frozen in time, has captured the imagination of people across generations, serving as a potent reminder of the enduring legacy of ancient civilizations.
In addition to its cultural impact, the Terracotta Army has played a pivotal role in shaping our understanding of ancient Chinese history and archaeology. The discovery of the army has led to significant advancements in the study of the Qin Dynasty, shedding light on its military organization, burial practices, and societal structure. Archaeological excavations at the site continue to yield new insights into the daily lives of ancient Chinese people, offering a glimpse into their beliefs, customs, and traditions.
Furthermore, the Terracotta Army has become a symbol of China’s cultural diplomacy and soft power on the global stage. Exhibitions featuring replicas of the army have toured major cities around the world, attracting millions of visitors and fostering greater cross-cultural understanding and appreciation. Through these exhibitions, the story of the Terracotta Army transcends national borders, bridging cultural divides and fostering connections between people from different backgrounds.
Ultimately, the legacy of the Terracotta Army serves as a testament to the enduring power of human creativity and ingenuity. From its construction over two millennia ago to its discovery in the 20th century and its continued study and preservation in the present day, the Terracotta Army stands as a testament to the resilience of ancient civilizations and the timeless quest for immortality and eternal glory. As we marvel at the silent guardians of an ancient empire, we are reminded of the profound impact that art, history, and culture can have on shaping the course of human civilization.
Conclusion

In conclusion, the Terracotta Army of Xi’an, China, stands as a remarkable testament to the ingenuity, ambition, and cultural richness of ancient Chinese civilization. From its construction over two millennia ago to its discovery in the 20th century and its enduring legacy in the present day, the army has captured the imagination of people worldwide, serving as a symbol of China’s rich cultural heritage and historical significance.
The discovery of the Terracotta Army has revolutionized our understanding of ancient Chinese history and archaeology, offering invaluable insights into the military, artistic, and cultural achievements of the Qin Dynasty. Its meticulous construction, intricate detail, and sheer scale continue to inspire awe and fascination, attracting millions of visitors to Xi’an each year and fostering greater cross-cultural understanding and appreciation.
Moreover, the legacy of the Terracotta Army extends beyond its historical significance to influence contemporary art, culture, and scholarship. Its iconic status has made it a source of inspiration for artists, filmmakers, and writers around the world, while its global exhibitions have served as a platform for cultural exchange and diplomacy.
As we marvel at the silent guardians of an ancient empire, we are reminded of the enduring power of human creativity and the timeless quest for immortality and eternal glory. The Terracotta Army stands as a testament to the resilience of ancient civilizations and the profound impact that art, history, and culture can have on shaping the course of human civilization. In preserving and studying the legacy of the Terracotta Army, we honor the achievements of our ancestors and ensure that their stories continue to inspire future generations.