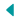
Guardian of the Horizon: Unveiling the Mystery of The Great Sphinx

Introduction
The Great Sphinx of Giza stands as an enigmatic sentinel, guarding the horizon of Egypt’s ancient land with its majestic presence. Carved from the bedrock of the Giza Plateau around 2500 BC, this colossal limestone statue has captivated the imagination of scholars, explorers, and tourists for centuries. Its significance transcends mere architecture; it embodies the enduring legacy of ancient Egyptian civilization and continues to inspire awe and curiosity in people around the world.
This monumental statue, with the body of a lion and the head of a human, symbolizes the fusion of divine power and earthly strength in ancient Egyptian culture. Positioned in close proximity to the Great Pyramids, it forms an integral part of the Giza Necropolis, a UNESCO World Heritage Site and one of the most iconic archaeological complexes on the planet. Yet, despite centuries of study and speculation, many mysteries still shroud the Sphinx, from its original purpose to the secrets hidden within its weathered features.
In this article, we embark on a journey to unravel the secrets of the Great Sphinx, exploring its historical context, physical attributes, cultural significance, and enduring legacy. From the sands of ancient Egypt to the halls of modern museums, we delve deep into the heart of this timeless monument, seeking to understand the mysteries that lie beneath its weathered facade.

Historical Context
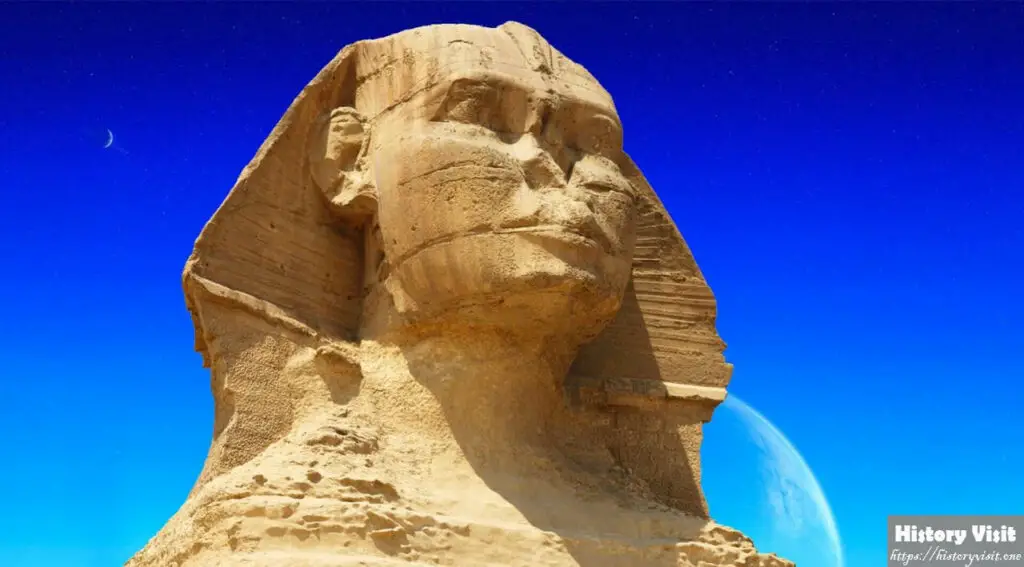
The Great Sphinx of Giza was crafted during the Old Kingdom of Egypt, a period of remarkable architectural innovation and cultural flourishing. Scholars believe it was built around 2500 BC during the reign of Pharaoh Khafre, who commissioned the construction of the nearby Pyramid of Khafre. The Sphinx’s location at the entrance of Khafre’s pyramid complex suggests a close connection between the two structures, possibly serving as a guardian or protective deity for the pharaoh’s tomb.
The construction of the Sphinx required immense manpower and engineering skill, as craftsmen carved the massive statue directly from the limestone bedrock of the Giza Plateau. Measuring approximately 73 meters (240 feet) in length and 20 meters (66 feet) in height, it is one of the largest monolithic statues in the world. Originally, the Sphinx would have been adorned with a colorful paint scheme, enhancing its imposing presence amidst the desert landscape.
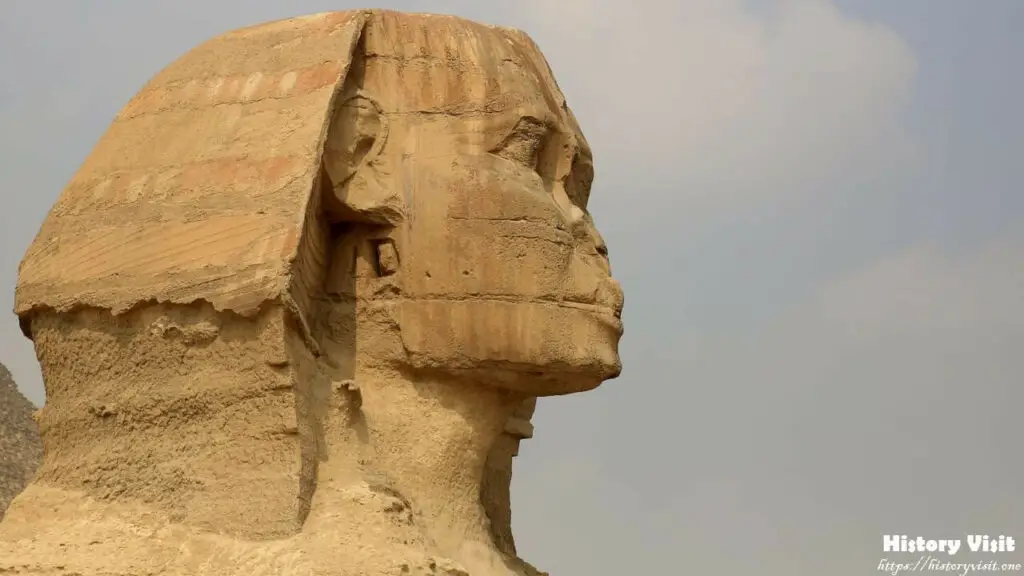
Despite its ancient origins, the Great Sphinx has endured centuries of natural erosion and human intervention, resulting in significant damage to its original features. The erosion patterns on the Sphinx’s body, particularly around its neck and shoulders, suggest prolonged exposure to wind and sandstorms over thousands of years. Additionally, the statue’s missing nose and beard have become enduring symbols of its mysterious past, fueling speculation and myth-making throughout history.
Physical Description

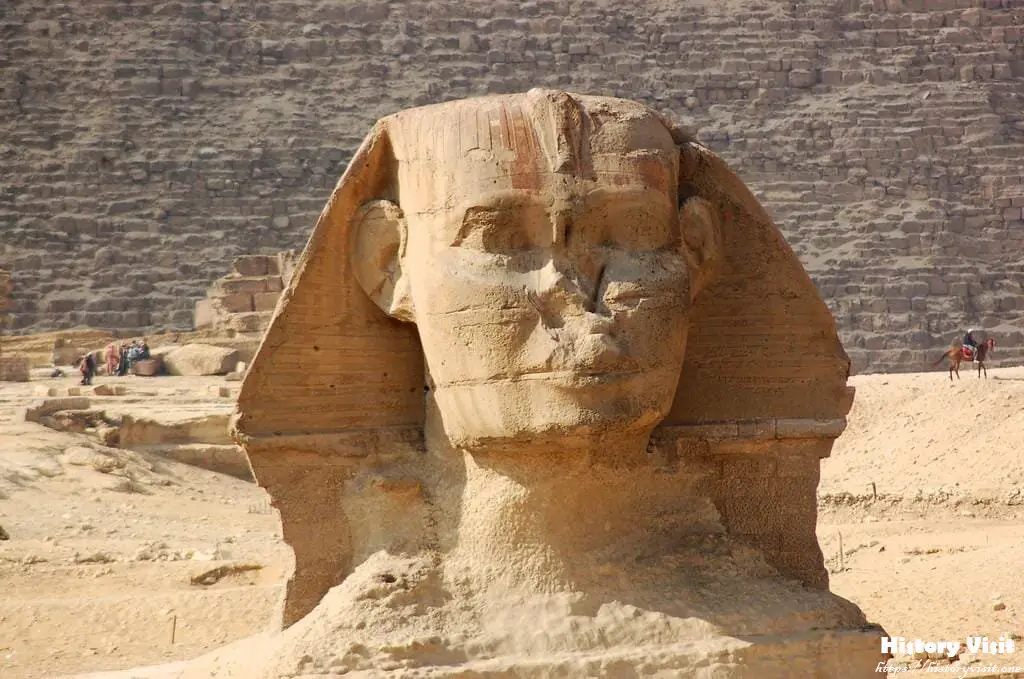
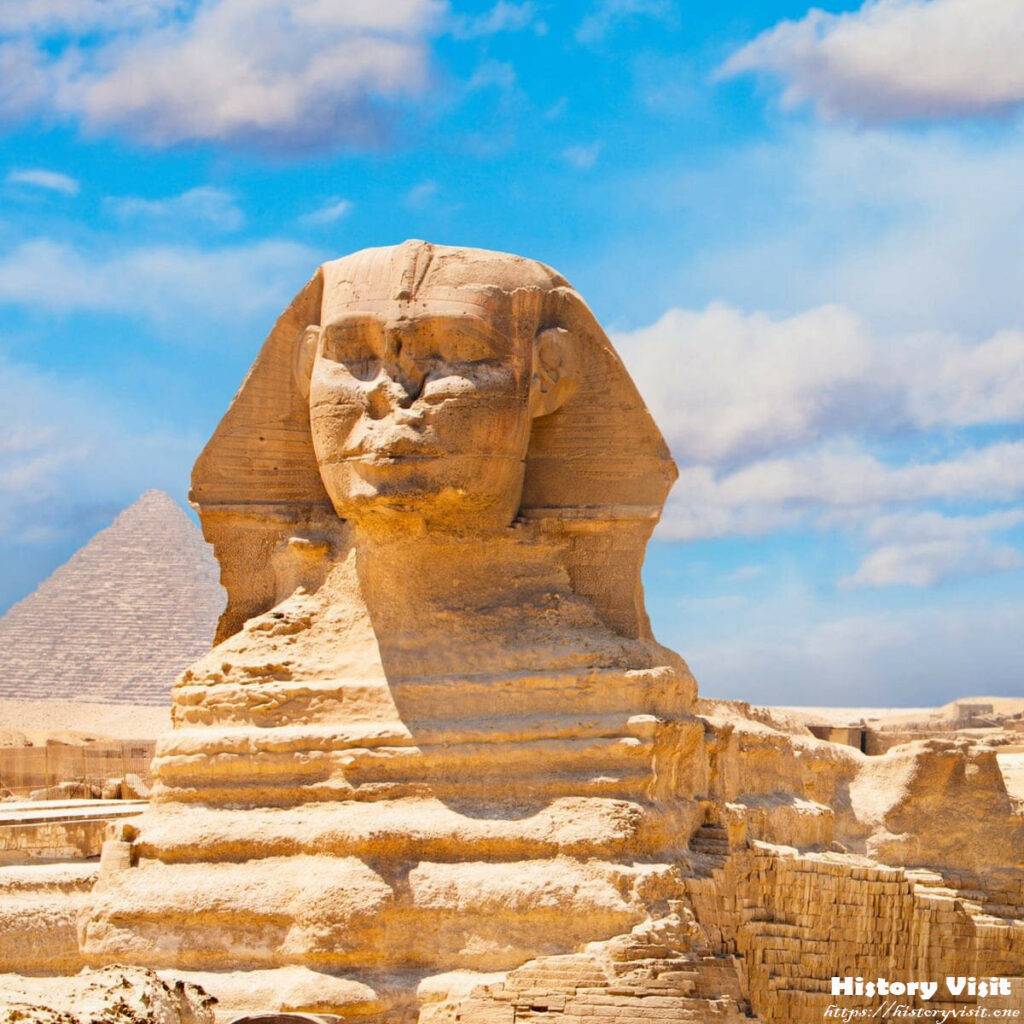
The Great Sphinx of Giza commands attention with its imposing size and striking appearance, combining the body of a lion with the face of a human. Carved with remarkable precision from the limestone bedrock of the Giza Plateau, the statue measures approximately 73 meters (240 feet) in length and 20 meters (66 feet) in height, making it one of the largest monolithic statues in the world. Its body, resembling the form of a reclining lion, extends along the desert landscape, while the head, adorned with the likeness of a pharaoh, gazes solemnly towards the eastern horizon.
The Sphinx’s face is believed to depict the likeness of Pharaoh Khafre, the ruler credited with commissioning its construction during the Old Kingdom of Egypt. Despite the erosion and damage sustained over millennia, traces of the statue’s original features remain, hinting at the craftsmanship and artistry of its ancient creators. The statue’s enigmatic expression, with its closed lips and inscrutable gaze, has inspired countless interpretations and speculations about its symbolic significance and hidden meaning.
Archaeological excavations around the Great Sphinx have revealed additional structures and features buried beneath the desert sands, including a temple complex and a causeway leading to the Pyramid of Khafre. These discoveries provide valuable insights into the original context and purpose of the Sphinx, suggesting that it played a central role in the religious and funerary rituals of ancient Egypt. Despite the passage of time and the ravages of nature, the Great Sphinx continues to stand as a testament to the ingenuity and artistic vision of its ancient creators.
Theories and Interpretations

The Great Sphinx of Giza has long been the subject of speculation and debate among scholars, archaeologists, and Egyptologists, who have proposed various theories to explain its origins, purpose, and significance. One of the most enduring mysteries surrounding the Sphinx is the question of its original appearance, particularly the presence of a ceremonial headdress or nemes headcloth worn by Egyptian pharaohs. While some researchers believe that the Sphinx was originally adorned with such regal attire, others argue that it may have been left unfinished or intentionally defaced at some point in history.
Another theory suggests that the Sphinx was constructed as a representation of the Egyptian sun god, Ra, symbolizing the cycle of death and rebirth associated with the solar deity. This interpretation is supported by the Sphinx’s orientation towards the rising sun on the spring equinox, aligning it with the celestial rhythms of the natural world. However, skeptics point out that the alignment may be purely coincidental, as similar phenomena can be observed with other structures in the region.
Perhaps the most intriguing theory regarding the Great Sphinx is the possibility of hidden chambers or passages concealed beneath its massive bulk. Over the centuries, numerous expeditions and excavations have sought to uncover these alleged secrets, fueled by legends of lost treasures and ancient knowledge hidden within the statue’s hollow interior. While some researchers remain skeptical of such claims, recent advancements in non-invasive imaging technology have reignited interest in the search for hidden chambers, promising new insights into the Sphinx’s enigmatic past.
Restoration and Preservation Efforts

Over the centuries, the Great Sphinx of Giza has weathered countless natural and human-induced challenges, from sandstorms and erosion to pollution and urban encroachment. In response to these threats, various restoration and preservation efforts have been undertaken to safeguard the statue’s structural integrity and historical significance. One of the most significant restoration projects took place in the early 20th century under the supervision of French archaeologist Émile Baraize, who conducted extensive excavations and repairs to stabilize the Sphinx’s deteriorating limestone structure.
In more recent years, the Egyptian government, in collaboration with international organizations and experts, has implemented comprehensive conservation initiatives aimed at mitigating the impact of environmental factors and human activity on the Great Sphinx and its surrounding environment. These efforts include measures such as installing protective barriers, monitoring erosion patterns, and implementing sustainable tourism practices to minimize the statue’s exposure to damage and degradation.
Despite these ongoing conservation efforts, the Great Sphinx continues to face challenges in preserving its cultural heritage in the face of modern development and environmental pressures. Rising groundwater levels, pollution, and urban expansion pose significant threats to the stability and longevity of the monument, underscoring the importance of continued vigilance and proactive measures to ensure its survival for future generations. By embracing innovative technologies and collaborative partnerships, we can honor the legacy of the Great Sphinx and protect this iconic symbol of ancient Egypt for centuries to come.
Cultural Legacy

The Great Sphinx of Giza holds a unique place in the cultural legacy of humanity, transcending its origins in ancient Egypt to become a global icon of mystery, power, and resilience. Throughout history, the Sphinx has captured the imagination of artists, writers, and adventurers, who have sought to unravel its secrets and pay homage to its enduring majesty.
In ancient Egypt, the Sphinx was revered as a guardian deity, believed to possess divine powers of protection and guidance. Its imposing presence at the entrance of the Giza Necropolis symbolized the pharaoh’s authority and connection to the gods, serving as a tangible expression of royal power and prestige. Over the centuries, the Sphinx became the subject of myth and legend, inspiring awe and reverence among the Egyptian people and leaving an indelible mark on their cultural identity.
As Egypt’s ancient civilization gave way to successive empires and cultures, the legacy of the Great Sphinx continued to resonate across time and space. From the conquests of Alexander the Great to the rise of the Roman Empire, the Sphinx remained a potent symbol of Egypt’s past glory and enduring spirit. Its enigmatic presence inspired awe and wonder in travelers and scholars from distant lands, who marveled at the skill and artistry of its ancient creators.
During the Renaissance period, the rediscovery of ancient Egyptian art and architecture sparked a renewed fascination with the Great Sphinx among European intellectuals and artists. From Leonardo da Vinci to Napoleon Bonaparte, countless luminaries of the era sought to unlock the secrets of the Sphinx and uncover the mysteries of Egypt’s ancient past. Their writings, paintings, and sculptures immortalized the Sphinx as a symbol of antiquity and wonder, shaping the collective imagination of generations to come.
In the modern era, the Great Sphinx has become a global icon of cultural heritage and archaeological significance, attracting millions of visitors from around the world each year. Its image adorns postcards, stamps, and souvenirs, serving as a powerful emblem of Egypt’s tourism industry and national identity. Yet, amid the crowds and clamor of modernity, the Sphinx remains a silent witness to the passage of time, a timeless sentinel guarding the secrets of the past.
As we reflect on the cultural legacy of the Great Sphinx of Giza, we are reminded of the enduring power of human creativity and ingenuity to transcend the boundaries of time and space. From its ancient origins to its modern-day prominence, the Sphinx continues to inspire awe and wonder in all who gaze upon its weathered features, reminding us of the profound mysteries that lie at the heart of the human experience. In its silent vigil atop the Giza Plateau, the Sphinx stands as a testament to the enduring legacy of ancient Egypt and the timeless quest for knowledge and understanding that unites us all.
Conclusion

In conclusion, the Great Sphinx of Giza stands as a timeless testament to the ingenuity, artistry, and cultural legacy of ancient Egypt. From its enigmatic origins in the sands of the Giza Plateau to its enduring presence in the global imagination, the Sphinx has captivated the hearts and minds of people for millennia. As we have explored in this article, the Sphinx represents far more than just a colossal statue; it embodies the spirit of a civilization that dared to dream on a grand scale and left behind monuments that continue to inspire wonder and curiosity in the modern world.
Despite the passage of time and the challenges of preservation, the Great Sphinx remains a symbol of resilience and endurance, weathering the ravages of nature and human intervention with quiet dignity. Its weathered features and silent gaze serve as a reminder of the impermanence of human endeavors and the enduring power of the past to shape the present. In its mysterious presence, the Sphinx invites us to ponder the mysteries of ancient Egypt and contemplate the broader mysteries of existence that transcend time and space.
As we gaze upon the Great Sphinx of Giza, we are reminded of the timeless quest for knowledge and understanding that unites humanity across cultures and civilizations. Whether as a symbol of divine power, a masterpiece of artistic craftsmanship, or a beacon of cultural heritage, the Sphinx continues to inspire awe and reverence in all who encounter it. In its silent vigil over the sands of Egypt, the Sphinx reminds us of the enduring legacy of the past and the boundless potential of the human spirit to reach for the stars.