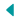
Grace and Power: The Winged Victory of Samothrace at the Louvre

Introduction
The Winged Victory of Samothrace, an exquisite masterpiece of Hellenistic sculpture, has captivated audiences for centuries. Located in the Louvre Museum in Paris, France, this majestic representation of Nike, the Greek goddess of victory, stands as a testament to the artistic brilliance and cultural significance of ancient Greece. Its dynamic pose, flowing drapery, and imposing presence create an enduring image of triumph and grace.
The journey of the Winged Victory of Samothrace from its creation in the 2nd century BC to its prominent place in the Louvre is a story of discovery, admiration, and meticulous preservation. This sculpture not only embodies the artistic innovations of its time but also reflects the cultural and historical context of the Hellenistic period, a time marked by great achievements in art and philosophy. As we delve into the history and significance of this iconic sculpture, we uncover layers of meaning and artistry that continue to inspire and awe.
Understanding the importance of the Winged Victory of Samothrace requires a comprehensive exploration of its origins, discovery, artistic features, and lasting impact. Through this journey, we gain insight into the profound connection between ancient art and contemporary appreciation, highlighting why this masterpiece remains a focal point of admiration in the world of art.
Historical Origins

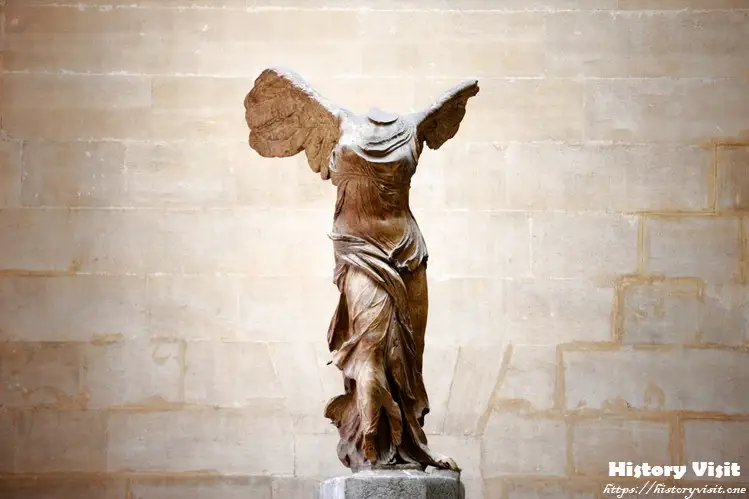
The Winged Victory of Samothrace was created in the 2nd century BC during the Hellenistic period, a time of significant cultural and artistic development in ancient Greece. This era, following the conquests of Alexander the Great, saw a blend of Greek traditions with influences from the diverse cultures within Alexander’s empire. The sculpture embodies the dynamism and expressiveness characteristic of Hellenistic art, capturing a moment of divine triumph.
Samothrace, the island where the sculpture was discovered, held religious significance in ancient Greece. It was home to the Sanctuary of the Great Gods, a site of mystery cults and significant religious rituals. The sanctuary attracted pilgrims from across the Greek world, seeking blessings and guidance from the gods. The Winged Victory, believed to be part of a larger naval monument, likely commemorated a significant naval victory, reflecting the island’s importance as a religious and cultural center.
Nike, the goddess depicted in the sculpture, symbolized victory in both war and peaceful competitions. Her representation in art served as a powerful reminder of the divine favor and glory that victory bestowed upon the victors. The creation of the Winged Victory of Samothrace thus not only celebrated a specific historical event but also embodied the broader cultural and religious significance of victory in ancient Greek society.
Discovery and Museum Journey

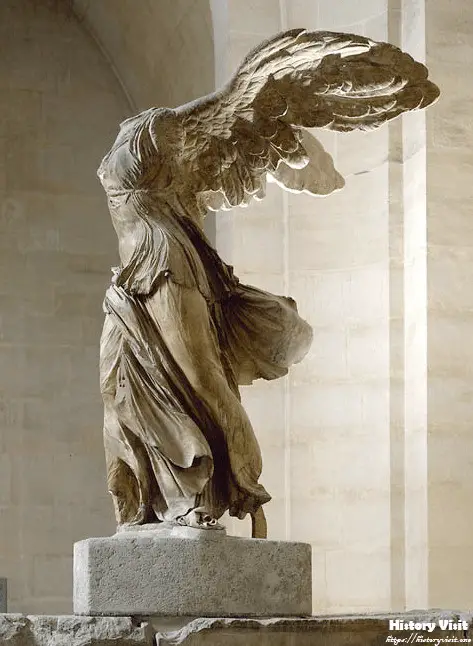
The Winged Victory of Samothrace was discovered in 1863 by French archaeologist Charles Champoiseau. Unearthed on the island of Samothrace, the sculpture was found in several fragmented pieces, buried within the ruins of the Sanctuary of the Great Gods. Champoiseau’s discovery was a momentous event, shedding light on the artistic achievements of the Hellenistic period and sparking interest in further archaeological exploration of the site.
Transporting the fragmented sculpture to Paris presented significant challenges. The marble pieces had to be carefully excavated, documented, and shipped across the Mediterranean to ensure their preservation. Once in Paris, the fragments underwent a meticulous restoration process, piecing together the statue to restore its original grandeur. The restored sculpture was eventually installed in the Louvre Museum, where it quickly became one of its most celebrated exhibits.
The Winged Victory’s installation in the Louvre marked a significant moment in the museum’s history. Placed prominently at the top of the Daru staircase, the sculpture commands attention and admiration from all who visit. Its imposing presence and dynamic form create a sense of awe, drawing visitors into the grandeur of ancient Greek art. The journey from Samothrace to the Louvre transformed the Winged Victory into an enduring symbol of artistic excellence and cultural heritage.
Artistic Elements
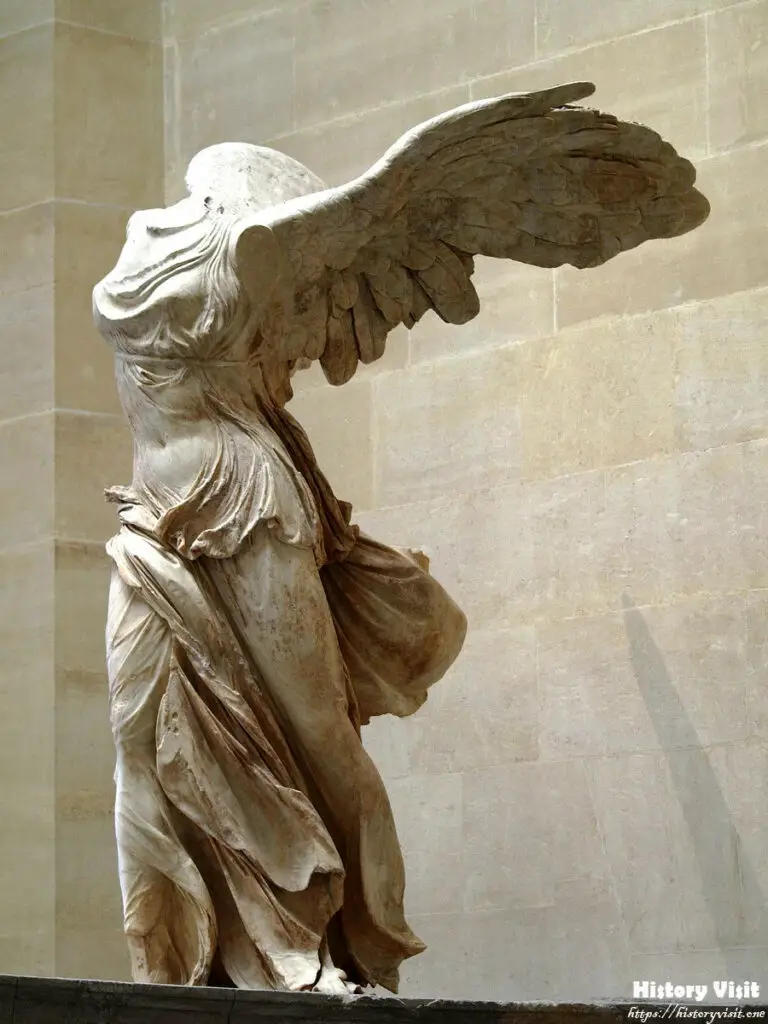

The Winged Victory of Samothrace is celebrated for its intricate artistic features that capture a sense of movement and vitality. The sculpture stands at approximately 8 feet tall, crafted from finely detailed marble. The figure’s pose, with wings outstretched and garments seemingly caught in the wind, creates a dynamic and powerful image of the goddess descending from the heavens to announce victory.
The drapery of the sculpture is particularly notable for its realism and intricacy. The folds of the garment cling to Nike’s body, accentuating her form while also conveying the sense of motion and the effect of wind. This masterful depiction of fabric creates a lifelike quality that draws viewers into the moment captured by the artist. The sense of motion is further enhanced by the forward thrust of the figure’s chest and the backward sweep of the wings.
The wings of the sculpture, though partially reconstructed, add to the overall impression of divine power and grace. The detailed carving of the feathers showcases the skill of the sculptor in rendering natural elements with precision. This combination of realistic detail and dynamic composition exemplifies the Hellenistic artistic style, which sought to convey not only physical form but also the emotional and dramatic intensity of the subjects depicted.
Symbolism and Meaning
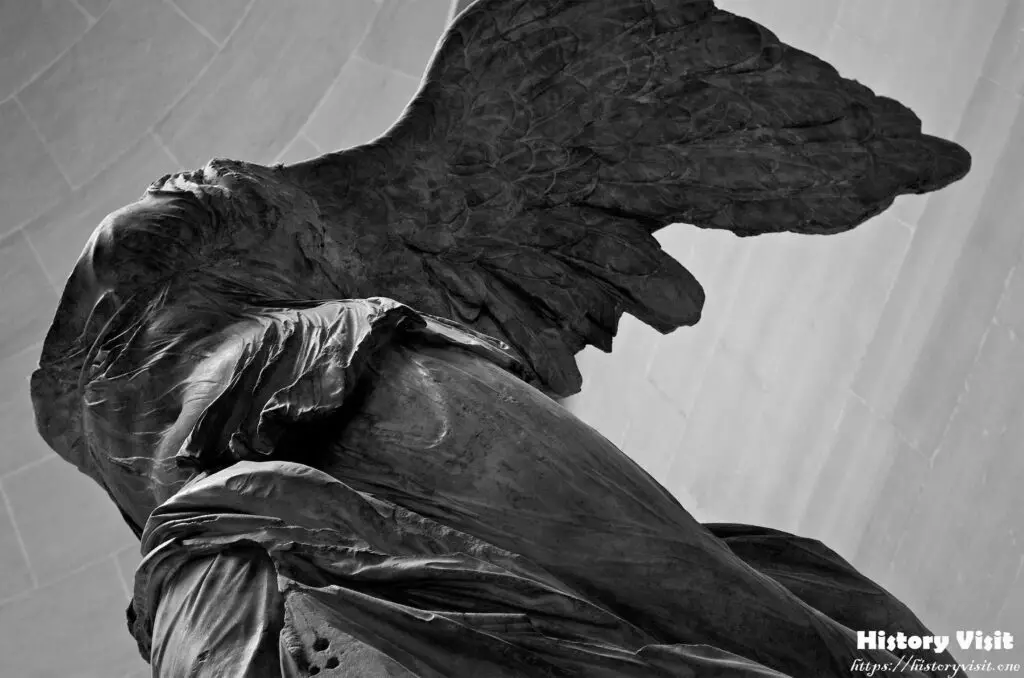

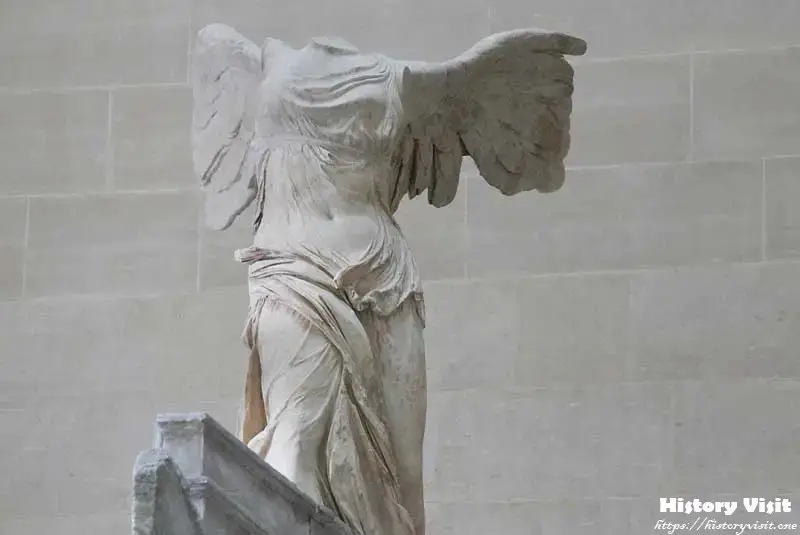
The Winged Victory of Samothrace is rich in symbolism, reflecting the cultural and religious values of ancient Greece. Nike, the goddess of victory, represents not just triumph in battle but also success in athletic and artistic competitions. Her depiction in the sculpture conveys the idea of divine favor and the exaltation of human achievements. The forward motion and outstretched wings suggest the moment of descent, as if she is arriving to bestow victory upon the deserving.
Interpretations of the sculpture often focus on its missing elements, such as the head and arms, which have never been recovered. Scholars speculate that Nike’s right arm might have been raised in a gesture of victory, while the left could have held a wreath or a trophy. The absence of these parts invites viewers to imagine the complete figure, engaging with the sculpture in a way that evokes its original grandeur and purpose.
The potential significance of the naval setting adds another layer of meaning to the sculpture. The base of the statue resembles the prow of a ship, indicating that it may have commemorated a naval victory. This connection to maritime triumphs aligns with the historical context of the Hellenistic period, when naval power was crucial to the success of Greek city-states. The Winged Victory thus stands as a symbol of both military and cultural supremacy, celebrating the achievements of its patrons.
Conservation Efforts

Preserving the Winged Victory of Samothrace has been a complex and ongoing process, reflecting the challenges and advancements in the field of art conservation. Early restoration efforts focused on reassembling the fragmented pieces, which required careful documentation and alignment to ensure the sculpture’s structural integrity. These initial restorations aimed to present the sculpture as close to its original form as possible, despite the missing elements.
Modern conservation techniques have further enhanced the preservation of the Winged Victory. Advances in materials and methods allow conservators to stabilize the sculpture and protect it from environmental damage. Regular assessments and maintenance are conducted to address issues such as marble deterioration and surface discoloration. The goal of these efforts is to ensure that the sculpture remains an enduring symbol of artistic excellence for future generations.
The role of the Louvre Museum in preserving the Winged Victory is paramount. The museum provides a controlled environment that mitigates the risks of temperature fluctuations, humidity, and pollutants. Additionally, the Louvre’s team of experts continuously researches and applies the latest conservation techniques, ensuring that the Winged Victory remains in pristine condition. The dedication to preserving this masterpiece highlights its significance as a cultural treasure and an icon of human artistic achievement.
Impact on Art and Culture

The Winged Victory of Samothrace has had a profound impact on art and culture, influencing generations of artists and captivating audiences worldwide. Its dynamic composition and lifelike details have inspired countless reproductions and interpretations in various artistic media, from paintings and sculptures to photography and digital art. The sculpture’s embodiment of motion and emotion set a precedent for future works, encouraging artists to explore new ways of depicting the human form and experience.
In popular culture, the Winged Victory has become a symbol of triumph and resilience. Its image is frequently used in logos, advertisements, and even as a motif in fashion and design. The sculpture’s enduring appeal lies in its ability to convey a universal message of victory and human achievement, transcending the boundaries of time and place. This widespread recognition underscores the sculpture’s significance as a cultural icon.
The Winged Victory’s presence in the Louvre further cements its status as a masterpiece of world heritage. Visitors from around the globe flock to see the sculpture, drawn by its storied history and artistic brilliance. The Louvre’s efforts to display and preserve the Winged Victory ensure that it continues to inspire and educate, serving as a bridge between ancient and modern artistic traditions. The sculpture’s impact on art and culture is a testament to its timeless beauty and enduring relevance.
Conclusion

The Winged Victory of Samothrace stands as a testament to the artistic and cultural achievements of ancient Greece. Its dynamic form, intricate details, and profound symbolism capture the essence of Hellenistic art, showcasing the skill and creativity of its creators. The sculpture’s journey from the island of Samothrace to its prominent place in the Louvre Museum reflects its enduring significance and the dedication to preserving this iconic masterpiece.
Understanding the historical context, artistic elements, and symbolic meanings of the Winged Victory allows us to appreciate its impact on both ancient and modern audiences. The sculpture’s influence on subsequent generations of artists and its presence in popular culture highlight its timeless appeal. As we continue to study and preserve the Winged Victory, we honor the legacy of those who created it and ensure that its message of triumph and grace endures.
In the halls of the Louvre, the Winged Victory of Samothrace remains a beacon of artistic excellence and cultural heritage. Its powerful depiction of divine victory continues to inspire awe and admiration, reminding us of the enduring legacy of ancient Greek art. As we stand before this magnificent sculpture, we are reminded of the timeless connection between past and present, and the enduring power of human creativity.