Elephant Hunting: A Threat to Our Natural Heritage
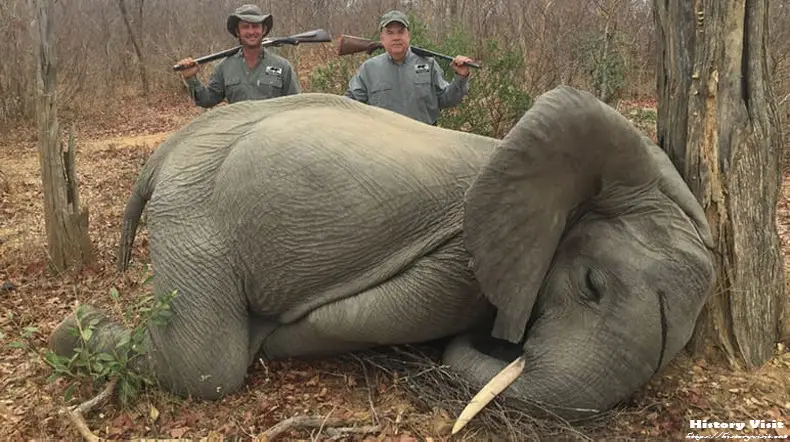

Introduction:
Elephant hunting stands as a grim testament to humanity’s unchecked exploitation of the natural world. As the earth’s largest land mammals, elephants have captivated the human imagination for centuries, yet their populations have suffered immensely at the hands of hunters. From the sprawling savannas of Africa to the dense jungles of Asia, the echoes of gunfire and the rustle of ivory trade have left a devastating impact on elephant numbers. As we delve deeper into the history, reasons, and consequences of elephant hunting, it becomes apparent that urgent action is needed to preserve these iconic creatures for future generations.
Present Elephant Population:
The current state of elephant populations paints a sobering picture of their decline. Despite conservation efforts, the global elephant population remains perilously low compared to historical levels. African elephants, once numbering in the millions, now hover around 415,000 individuals, with their Asian counterparts facing an even more precarious situation at roughly 40,000 individuals. Habitat loss, human-elephant conflict, and rampant poaching continue to exact a heavy toll on these magnificent animals, pushing them closer to the brink of extinction.
Comparing these figures to historical records reveals the extent of the decline. Just a century ago, vast herds of elephants roamed freely across the African and Asian continents, shaping their ecosystems and inspiring awe in all who beheld them. Yet, relentless hunting for ivory and other commodities, coupled with habitat destruction and fragmentation, has led to a staggering loss of biodiversity. The rapid decline in elephant populations not only signals a loss of natural heritage but also underscores the urgent need for coordinated conservation efforts to reverse this trend.
History of Elephant Hunting:
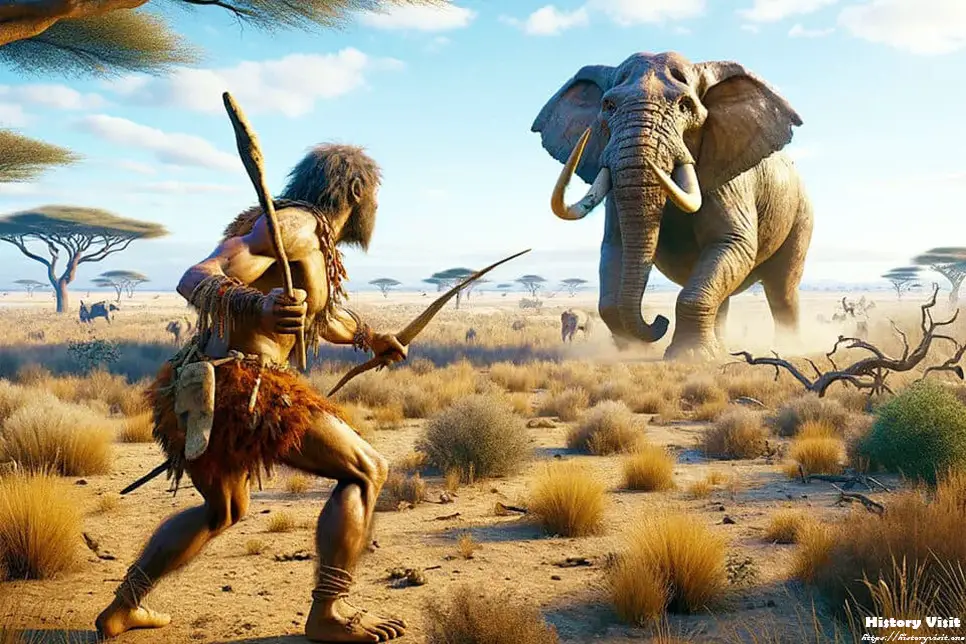

The history of elephant hunting is as old as human civilization itself. From ancient civilizations to colonial powers, elephants have been coveted for their tusks, meat, and sheer grandeur. In ancient times, rulers flaunted their wealth and power through displays of captured elephants, while ivory served as a prized commodity for luxury goods and ornamentation. However, it was during the colonial era that elephant hunting reached its zenith, driven by the insatiable demand for ivory in Europe and beyond. Colonial powers exploited elephant populations with ruthless efficiency, decimating herds and wreaking havoc on ecosystems in the name of profit and power.
As the ivory trade flourished, so too did the methods of hunting. From traditional spears and arrows to modern firearms and helicopters, hunters employed increasingly sophisticated techniques to pursue their prey. The consequences were devastating, with entire elephant populations wiped out in a relentless pursuit of profit. The era of indiscriminate slaughter left scars on the landscape and the collective conscience of humanity, prompting calls for conservation and regulation in the latter half of the 20th century. Despite these efforts, elephant hunting continues to pose a significant threat to their survival, driven by persistent demand for ivory and other illicit goods.
Reasons for Elephant Hunting:
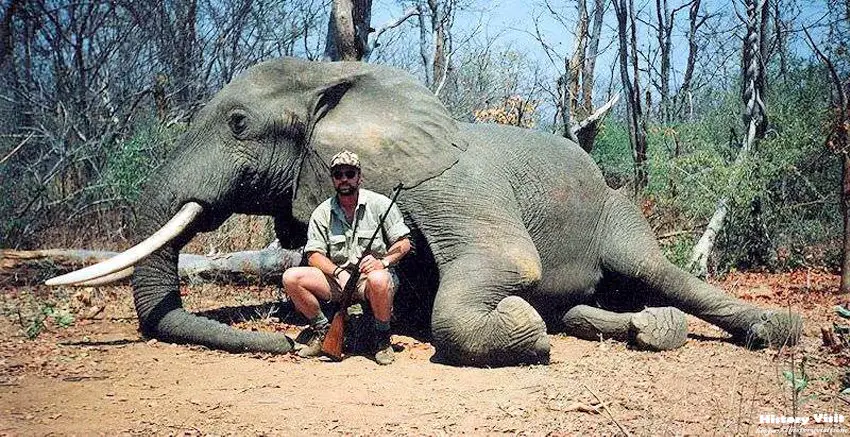

The motivations behind elephant hunting are multifaceted, encompassing economic, cultural, and environmental factors. At the heart of the issue lies the demand for ivory, driven by its perceived value as a status symbol and luxury commodity. Despite international bans on the ivory trade, illicit markets continue to thrive, fueled by consumer demand in Asia and other regions. Poaching remains a lucrative business for criminal syndicates, who exploit weak law enforcement and corrupt officials to smuggle ivory across borders.
In addition to ivory, elephants face other threats stemming from human activities. Habitat loss and fragmentation due to agriculture, infrastructure development, and urban expansion have encroached upon elephant habitats, leading to increased human-elephant conflicts. As elephants venture into human settlements in search of food and water, they often clash with farmers, resulting in loss of life and property on both sides. In some cases, retaliatory killings further exacerbate the problem, perpetuating a cycle of violence that threatens the survival of both elephants and humans.
Trophy hunting also poses a significant threat to elephant populations, particularly in Africa where it is still legal in some countries. Wealthy tourists pay exorbitant fees for the chance to hunt elephants for sport, perpetuating a culture of exploitation and commodification of wildlife. Despite arguments that trophy hunting contributes to conservation efforts and local economies, evidence suggests that it undermines long-term conservation goals by removing key individuals from elephant populations and disrupting social structures.
Value and Importance of Elephants:
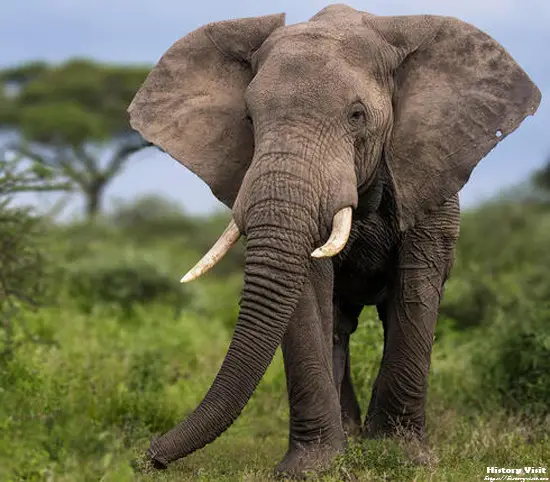

The value of elephants extends far beyond their monetary worth or ecological significance. As sentient beings with complex social structures and behaviors, elephants play a crucial role in shaping their environments and maintaining ecosystem health. Their feeding habits, for example, help to control vegetation growth and create habitats for other species, while their dung serves as a source of nutrients for soil and plants. Furthermore, elephants are keystone species, meaning that their presence or absence has a disproportionate impact on the ecosystems in which they live.
Beyond their ecological role, elephants hold immense cultural and symbolic value for many societies. Revered for their intelligence, strength, and longevity, elephants feature prominently in folklore, mythology, and religious traditions around the world. In many cultures, elephants are seen as symbols of wisdom, power, and spiritual connection, embodying the essence of the natural world and our place within it. Their majestic presence evokes a sense of wonder and reverence that transcends cultural boundaries, reminding us of the interconnectedness of all life on earth.
Protecting Elephants for Future Generations:

Safeguarding elephants requires a multifaceted approach that addresses the root causes of their decline while also promoting coexistence between humans and wildlife. Conservation efforts must prioritize the protection of elephant habitats, including the establishment of wildlife corridors and protected areas where elephants can roam freely without fear of persecution. Community-based conservation initiatives, which engage local communities in conservation efforts and provide alternative livelihoods, are essential for promoting sustainable development and reducing human-elephant conflicts.
At the same time, addressing the demand for ivory and other wildlife products is crucial for disrupting the illegal trade networks that drive poaching and trafficking. This requires robust law enforcement efforts, strengthened regulations, and international cooperation to dismantle criminal syndicates and hold traffickers accountable for their actions. Education and awareness-raising initiatives are also vital for fostering a culture of conservation and instilling values of respect and empathy towards elephants and other wildlife.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, elephant hunting represents a grave threat to the survival of these iconic animals and the ecosystems they inhabit. From ancient civilizations to modern-day societies, humanity’s exploitation of elephants has exacted a heavy toll on their populations and pushed them to the brink of extinction. Yet, there is hope. By taking decisive action to end elephant hunting, protect their habitats, and promote coexistence between humans and wildlife, we can ensure a future where elephants continue to roam the earth, enriching our lives and inspiring awe for generations to come. The time to act is now, for the sake of elephants, our natural heritage, and the health of our planet.